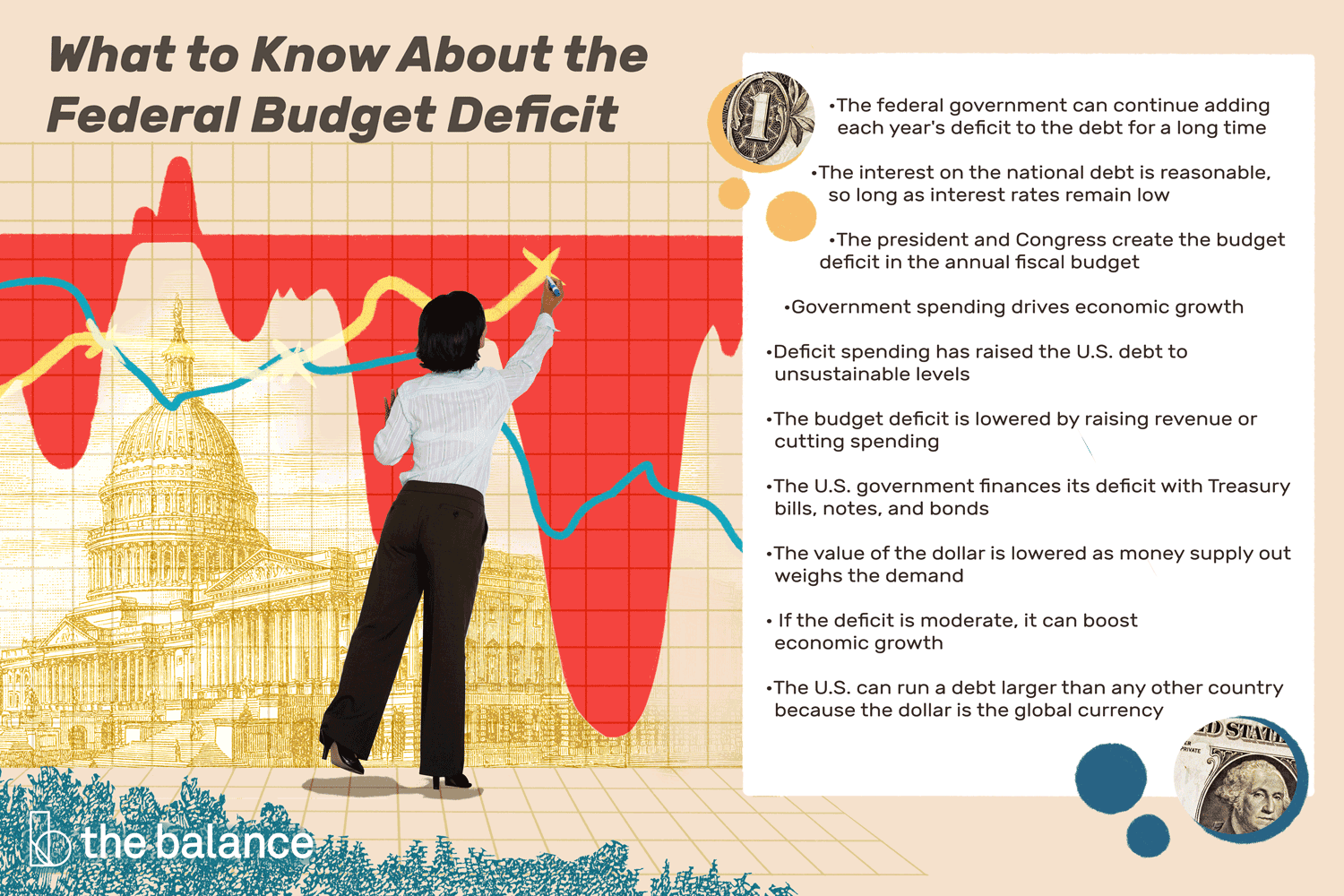
President Biden went big in his $6.8 trillion annual budget proposal to Congress by calling for $5 trillion in tax increases over the next decade, more than what lawmakers expected after the president downplayed his tax agenda in earlier meetings. It’s a risky move for the president as he heads into a tough reelection campaign in 2024.
Senate Democrats will have to defend 23 seats next year, including in Republican-leaning states such as Ohio, Montana and West Virginia, and Americans are concerned about inflation and the direction of the economy.
Republicans say Biden’s budget plan marks the return of tax-and-spend liberal politics; they warn higher taxes on corporations and the wealthy will hurt the economy. Biden, however, thinks he can win the debate by pledging that he won’t raise taxes on anyone who earns less than $400,000 a year.
Sen. Mike Crapo (R-Idaho), the ranking member of the Senate Finance Committee, called Biden’s ambitious tax plan “jaw-dropping.”
“This is exactly the wrong approach to solving our fiscal problems,” he said of the $5 trillion aggregate total of proposed tax hikes. “I think this sets a new record, by far.”
Grover Norquist, the president of Americans for Tax Reform, a group that advocates for lower taxes, said “in dollar terms, it’s the largest tax increase in American history.”
A surprise and a ‘negotiating position’
Many lawmakers were expecting Biden to propose between $2 trillion and $2.5 trillion in tax increases, based on what he said in his State of the Union address on Feb. 7 and on what media outlets reported in the days before the White House unveiled its budget plan.
The $5 trillion in new tax revenues is more than what the president called for last year, when Democrats controlled the House and Senate.
In October of 2021, when Biden was trying to nail down a deal with Sen. Joe Manchin (D-W.Va.) on the Build Back Better agenda, he proposed a more modest $2 trillion in tax increases.
The headline number even surprised some Democratic policy experts, though they agree the federal government needs to collect more revenue.
“I didn’t expect to see a number that big, but I’m not alarmed by it. I think it’s a negotiating position,” said Jim Kessler, the executive vice president for policy at Third Way, a centrist Democratic think tank.
Biden told lawmakers at his State of the Union address that his budget plan would lower the deficit by $2 trillion and that he would “pay for the ideas I’ve talked about tonight by making the wealthy and big corporations begin to pay their fair share.”
The president then surprised lawmakers with a budget proposal to cut $3 trillion from deficit over the next decade and to do it almost entirely by raising tax revenues.
Biden has called for a 25 percent tax on the nation’s wealthiest 0.01 percent of families. He has proposed raising the corporate tax rate from 21 percent to 28 percent and the top marginal income tax rate from 37 percent to 39.6 percent. He wants to quadruple the 1 percent tax on stock buybacks. He has proposed taxing capital gains at 39.6 percent for people with income of more than $1 million.
Kessler noted that Biden’s budget doesn’t include significant spending cuts nor does it reform Social Security, despite Biden’s pledge during the 2020 election to reduce the program’s imbalance. Kessler defended the president’s strategy of focusing instead on taxing wealthy individuals and corporations.
“The amount of unrealized wealth that people have at the top dwarfs anything that we’ve ever seen in the past,” he said. “These are opening bids” ahead of the negotiations between Biden and Speaker Kevin McCarthy (R-Calif.) to raise the debt limit.
Senate Republicans are trying to chip away at Biden’s argument that his tax policy will only hit wealthy individuals and companies. “It’s probably not good for the economy. Last time I checked, most tax increases on the business side are passed on to consumers, and I think we need to control spending more than adding $5 trillion in new taxes,” said Sen. Lindsey Graham (R-S.C.).
Norquist, the conservative anti-tax activist, warned that if enacted, raising the corporate tax rate would reverberate throughout the economy. “The corporate income tax, 70 percent of that is paid by workers and lower wages,” he said.
He said raising the top marginal tax rate and capital gains tax rate would hit small businesses that file under subchapter S of the tax code. “When you raise the top individual rate, you’re raising taxes on millions of smaller businesses in the United States,” he said. “Their employees end up paying that because that’s money they don’t have in the business anymore.”
How does Biden compare to predecessors?
Norquist noted that Obama and Clinton both cut taxes during their administrations, citing Clinton’s role in cutting the capital gains rate and Obama’s role in making many of the Bush-era tax cuts permanent. “Both of them ran a more moderate campaign. This guy is going Bernie Sanders,” he said of Biden, comparing him to the liberal independent senator from Vermont.
Biden’s budget is a significant departure from the approach then-President Obama took 12 years ago, when he also faced a standoff with a GOP-controlled House over the debt.
In his first year working with a House GOP majority, Obama in his fiscal 2012 budget proposed cutting the deficit by $1.1 trillion, of which he said two-thirds should come from spending cuts and one-third from tax increases. Obama later ramped up his proposal in the fall of 2011 by floating a plan to cut the deficit by $3.6 trillion over a decade and raise taxes by $1.6 trillion during that span.
Concerning for some Democrats
Republican strategists say they’ll use Biden’s proposed tax increases as ammunition against Democratic incumbents up for reelection next year. National Republican Senatorial Committee Chairman Steve Daines (Mont.) said Biden’s budget provides “a contrast” ahead of the election.
Sen. Jon Tester (D-Mont.), who faces a tough re-election in a state that former President Trump with 57 percent of the vote, said he’s leery about trillions of dollars in new taxes.
Asked last week if he’s worried about how Montanans might react to Biden’s proposed tax increases, Tester replied: “For sure. I got to make sure that will work. I just got to see what he’s doing.”
McCaul says Jan. 6 tapes not going to show ‘tourism at the Capitol’ Porter on Silicon Valley Bank collapse: ‘You can’t bet on’ interest rates staying low forever
Manchin, who is up for reelection in another red state, has called on his fellow Democrats to focus more on how the federal budget has swelled from $3.8 trillion in 2013 to $6.7 trillion today.
“Can we just see if we can go back to normal? Where were we before COVID? What was our trajectory before that?” he asked in a CNN interview Thursday. “How did it grow so quickly? How do we have so many things that are so necessary that weren’t before?” he said of the federal budget and debt.
The White House branded the House Freedom Caucus’ deficit plan as “tax breaks for the super wealthy and wasteful spending for special interests,” as the two sides continued to trade jabs amid an escalating debt ceiling battle.
“MAGA House Republicans are proposing, if spread evenly across affected discretionary programs, at least a 20 [percent] across the board cut,” White House Communications Director Ben LaBolt said in an initial analysis of the proposal.
LaBolt pointed to several typically Republican issue areas that would be impacted by such cuts, including law enforcement, border security, education and manufacturing.
“The one thing MAGA Republicans do want to protect are tax cuts for the super-wealthy,” he added. “This means that their plan, with all of the sacrifices they are asking of working-class Americans, will reduce the deficit by…$0.”
The Freedom Caucus on Friday unveiled its initial spending demands for a possible debt ceiling increase, as the potential for default looms this summer. The proposal would cap discretionary spending at fiscal 2022 levels for 10 years, resulting in a $131 billion cut from current levels. Defense spending would be maintained at current levels.
LaBolt claimed that the proposal would also defund police and make the border less secure, turning around two accusations that Republicans have frequently lobbed at the Biden administration.
Such spending cuts would, according to LaBolt’s analysis, eliminate funding for 400 state, local and tribal police officers and several thousand FBI agents and personnel and “deny the men and women of Customs and Border Protection the resources they need to secure our borders.”
He also criticized the Freedom Caucus’s calls to end President Biden’s student loan forgiveness plan and to rescind unspent COVID-19 and Inflation Reduction Act funds, claiming they would increase prescription drug and energy costs and ship manufacturing jobs overseas.
The analysis also accused the group of hard-line conservatives of making plans that would actually increase the federal deficit by $114 billion, and allow “the wealthy and big corporations to continue to cheat on their taxes.” Biden’s $6.8 trillion budget released on Thursday included tax hikes on the wealthy.
LaBolt’s 20 percent number represents a slight adjustment from Biden’s claim on Friday that the plan would require a 25 percent cut in discretionary spending across the board.
“If what they say they mean, they’re going to keep the tax cuts from the last president … no additional taxes on the wealthy — matter of fact reducing taxes — and in addition to that, on top of that, they’re going to say we have to cut 25 percent of every program across the broad,” Biden said during remarks on the economy. “I don’t know what there’s much to negotiate on.”
House Freedom Caucus Chairman Scott Perry (R-Pa.) hit back at the president on Friday, accusing him of misrepresenting their proposal. “For him to mention things like firefighters, police officers and health care — obviously, either he didn’t watch the press conference, he can’t read, or someone is, you know, got their hand up his back and they’re speaking for him, because those are just abject lies,” Perry told The Hill. “It’s the same old, you know, smear-and-fear campaign by the Biden administration.” (Courtesy: CNN)































 Luxury Jewelry is well-known for its sophisticated designs and utilization of the most precious and uncommon unrefined substances. The Luxury Jewelry Market is vigorous and quickly developing. It’s also exceptionally divided and determined by buyer conduct and style. In the nearing years, huge market development is normal, from increasing extra cash and amplifying buyer consumption of extravagant merchandise. Assimilating the luxury gems industry with diversion and allure businesses has set new open doors for the market.
Luxury Jewelry is well-known for its sophisticated designs and utilization of the most precious and uncommon unrefined substances. The Luxury Jewelry Market is vigorous and quickly developing. It’s also exceptionally divided and determined by buyer conduct and style. In the nearing years, huge market development is normal, from increasing extra cash and amplifying buyer consumption of extravagant merchandise. Assimilating the luxury gems industry with diversion and allure businesses has set new open doors for the market.
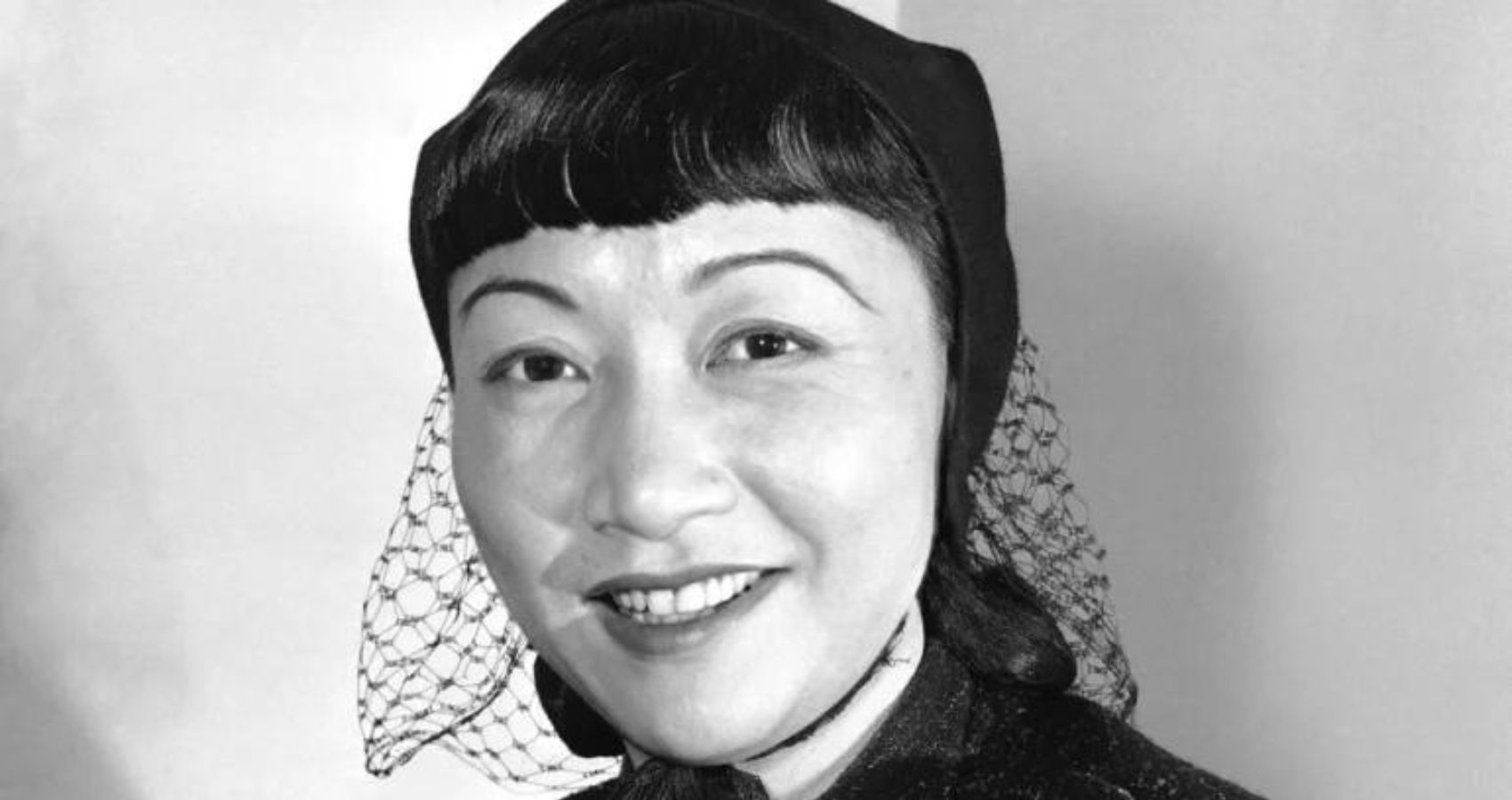


























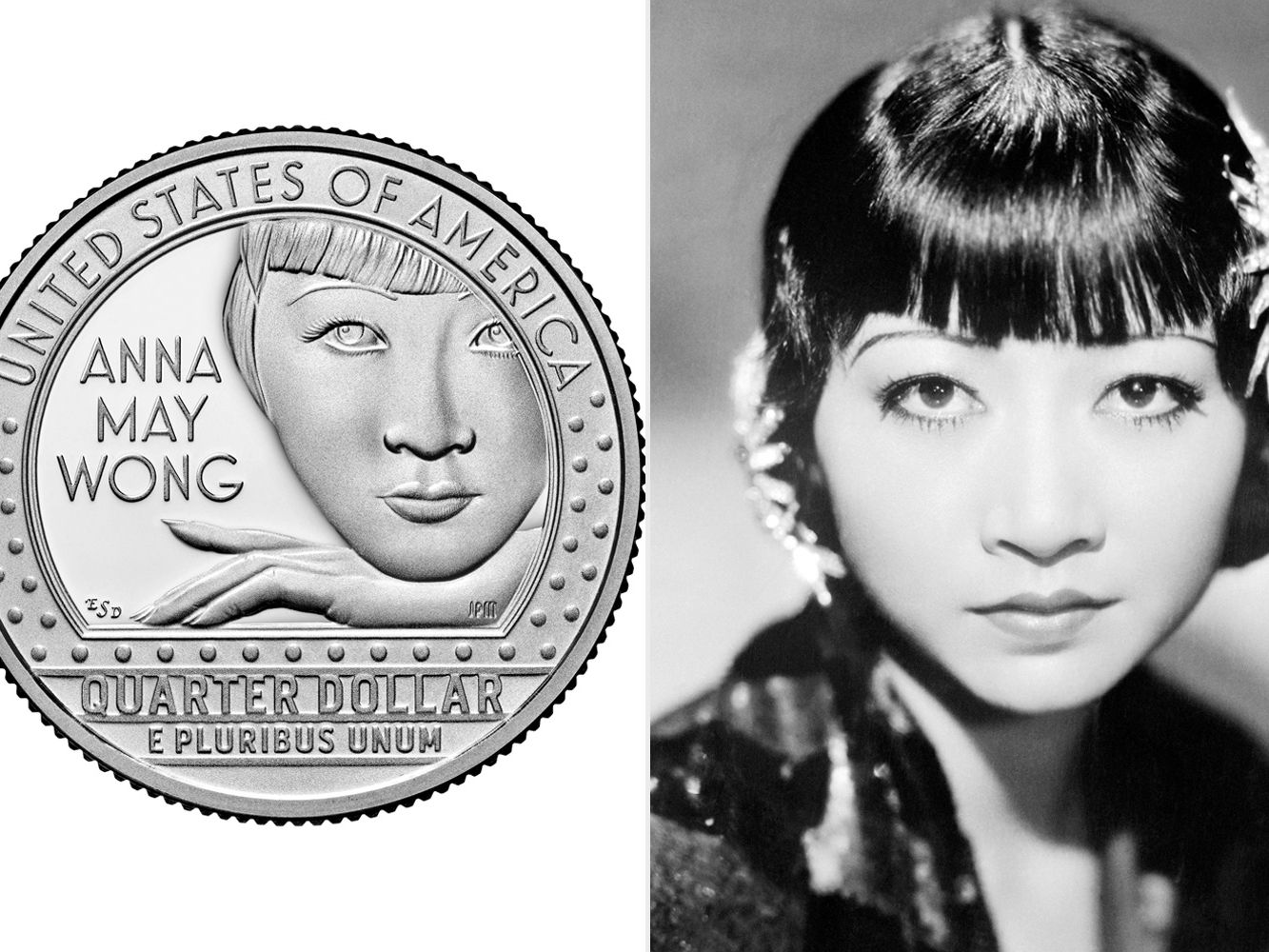 Born in Los Angeles, she began acting at 14 and took a lead role in “The Toll of the Sea” three years later, in 1922. She went on to appear in dozens of movies but faced deeply entrenched racism in Hollywood, where she struggled to break from stereotypical roles.
Born in Los Angeles, she began acting at 14 and took a lead role in “The Toll of the Sea” three years later, in 1922. She went on to appear in dozens of movies but faced deeply entrenched racism in Hollywood, where she struggled to break from stereotypical roles.



 The Education Department’s technical team will be responding to potential issues in real-time, and although the application itself won’t change, the team may make changes to the website if faced with any glitches.
The Education Department’s technical team will be responding to potential issues in real-time, and although the application itself won’t change, the team may make changes to the website if faced with any glitches. 








 The dollar is also soaring in destinations like Thailand, India and South Korea — countries with ample tourism interest from Americans and relatively weaker economic growth than the U.S.
The dollar is also soaring in destinations like Thailand, India and South Korea — countries with ample tourism interest from Americans and relatively weaker economic growth than the U.S. 
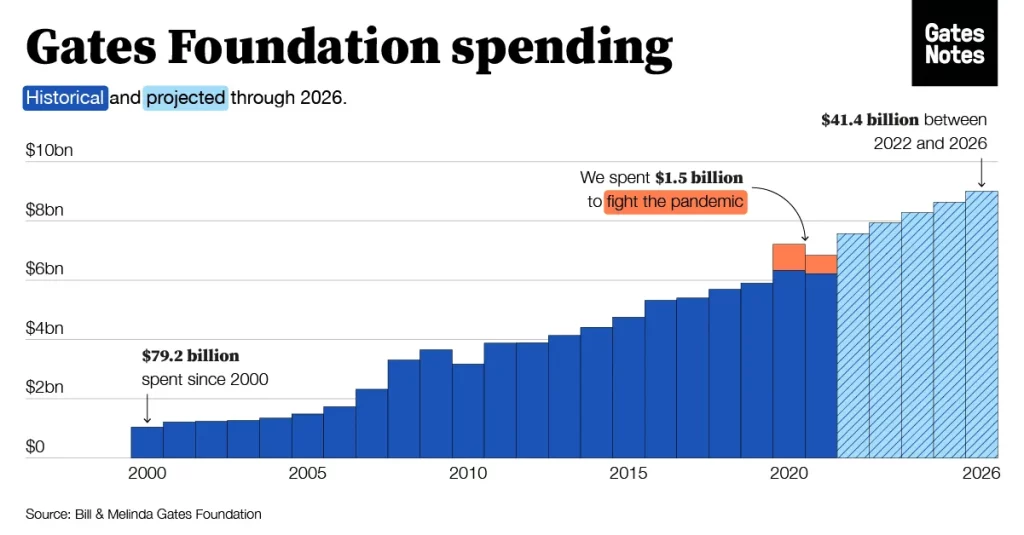 Bill Gates is moving $20 billion of his wealth into the endowment of the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, which is ramping up its spending in the face of global challenges, including the pandemic and the war in Ukraine, media reports said.
Bill Gates is moving $20 billion of his wealth into the endowment of the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, which is ramping up its spending in the face of global challenges, including the pandemic and the war in Ukraine, media reports said.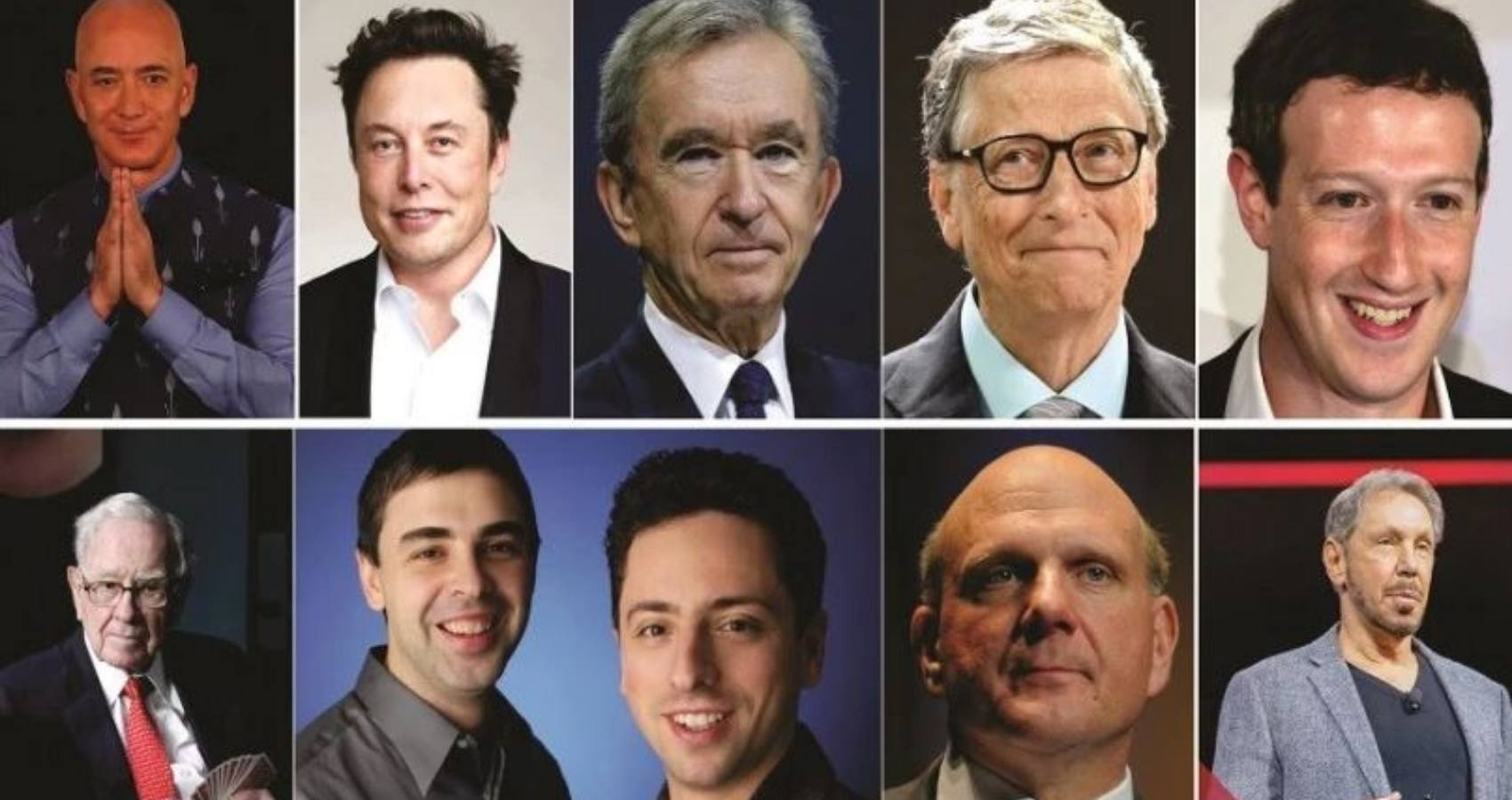 
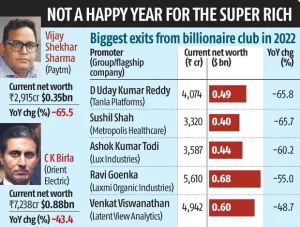
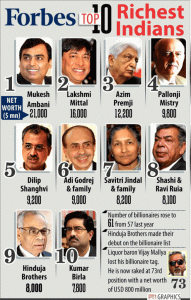 It’s a sharp departure from the previous two years, when the fortunes of the ultra-rich swelled as governments and central banks unleashed unprecedented stimulus measures in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic, juicing the value of everything from tech companies to cryptocurrencies.
It’s a sharp departure from the previous two years, when the fortunes of the ultra-rich swelled as governments and central banks unleashed unprecedented stimulus measures in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic, juicing the value of everything from tech companies to cryptocurrencies.
 At least at first,
At least at first, 
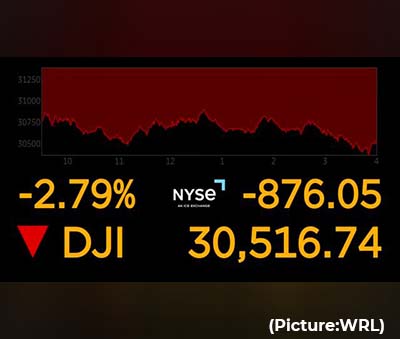 “After holding their breath for nearly a week awaiting the US CPI report for May, investors exhaled in exasperation as inflation came in hotter than expected,” Sam Stovall, chief investment strategist at CFRA, said in a note to clients Monday morning.
“After holding their breath for nearly a week awaiting the US CPI report for May, investors exhaled in exasperation as inflation came in hotter than expected,” Sam Stovall, chief investment strategist at CFRA, said in a note to clients Monday morning.
 He said that when Berkshire’s stock fell, there was nothing wrong with the company. He said that the mind of the investor should be right. Otherwise, your life will be spent in buying and selling shares at the wrong time and you will continue to cry for loss. Investors take decisions on the advice of others when prices fluctuate.
He said that when Berkshire’s stock fell, there was nothing wrong with the company. He said that the mind of the investor should be right. Otherwise, your life will be spent in buying and selling shares at the wrong time and you will continue to cry for loss. Investors take decisions on the advice of others when prices fluctuate.
 Billionaires have seen their total
Billionaires have seen their total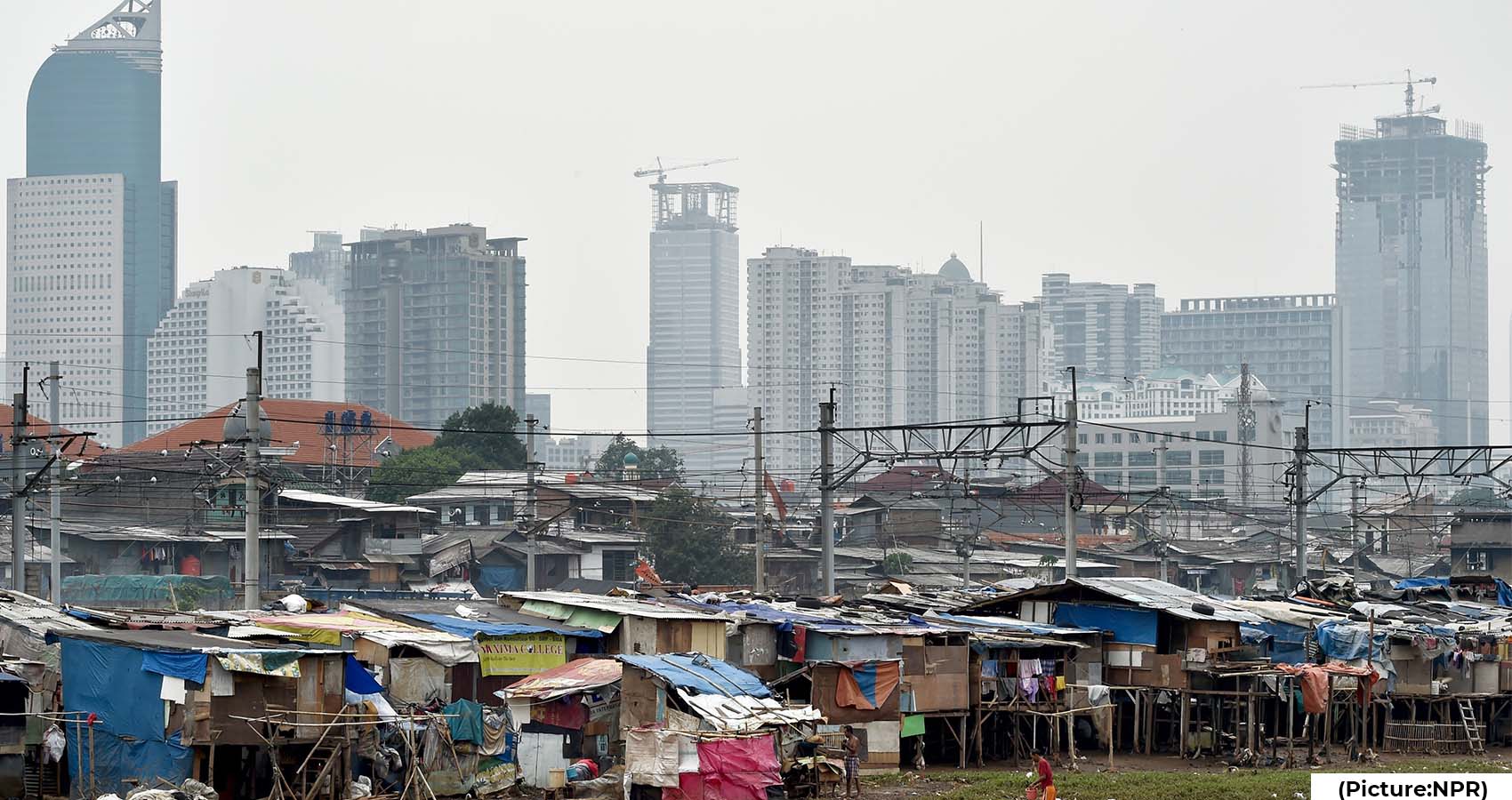 
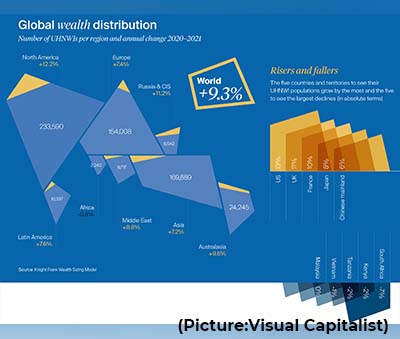 The fortunes of food and energy billionaires have risen by $453 billion in the last two years, equivalent to $1 billion every two days, says Oxfam.
The fortunes of food and energy billionaires have risen by $453 billion in the last two years, equivalent to $1 billion every two days, says Oxfam.

 Toyota is aligning its own green targets with India’s ambitions of becoming a manufacturing hub though the switch to clean transport in the South Asian nation is slower than other countries such as China and the U.S. Expensive price tags, lack of options in electric models and insufficient charging stations have led to sluggish adoption of battery vehicles in India.
Toyota is aligning its own green targets with India’s ambitions of becoming a manufacturing hub though the switch to clean transport in the South Asian nation is slower than other countries such as China and the U.S. Expensive price tags, lack of options in electric models and insufficient charging stations have led to sluggish adoption of battery vehicles in India.

 Central to bitcoin’s technology is the process through which transactions are verified and then recorded on what’s known as the blockchain. Computers connected to the bitcoin network race to solve complex mathematical calculations that verify the transactions, with the winner earning newly minted bitcoins as a reward. Currently, when a machine solves the puzzle, its owner is rewarded with 6.25 bitcoins — worth about $260,000 total. The system is calibrated to release 6.25 bitcoins every 10 minutes.
Central to bitcoin’s technology is the process through which transactions are verified and then recorded on what’s known as the blockchain. Computers connected to the bitcoin network race to solve complex mathematical calculations that verify the transactions, with the winner earning newly minted bitcoins as a reward. Currently, when a machine solves the puzzle, its owner is rewarded with 6.25 bitcoins — worth about $260,000 total. The system is calibrated to release 6.25 bitcoins every 10 minutes.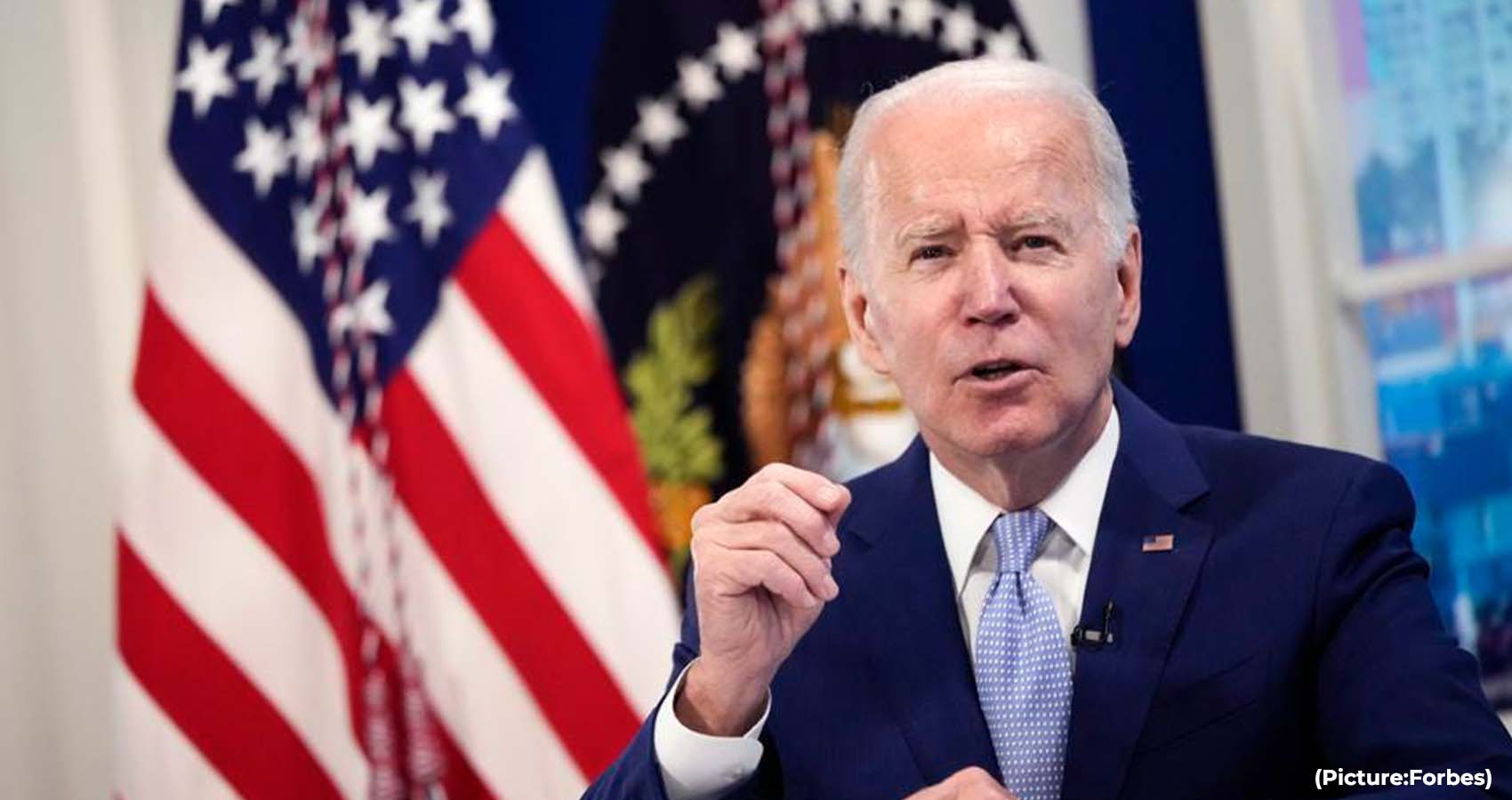


 Murthy is said to own a 0.9 per cent stake in Infosys, which has been calculated as being worth 500 million pounds. Annual dividends from this holding is estimated to be 11.6 million pounds. On Thursday, it emerged she pays just 30,000 pounds a year in the UK on the British income.
Murthy is said to own a 0.9 per cent stake in Infosys, which has been calculated as being worth 500 million pounds. Annual dividends from this holding is estimated to be 11.6 million pounds. On Thursday, it emerged she pays just 30,000 pounds a year in the UK on the British income.
 “Expectation is that inflation could remain elevated following the recent rise in energy and food prices. On the other hand, industrial production could grow at a slower pace in January and could further weigh on the currency.”
“Expectation is that inflation could remain elevated following the recent rise in energy and food prices. On the other hand, industrial production could grow at a slower pace in January and could further weigh on the currency.”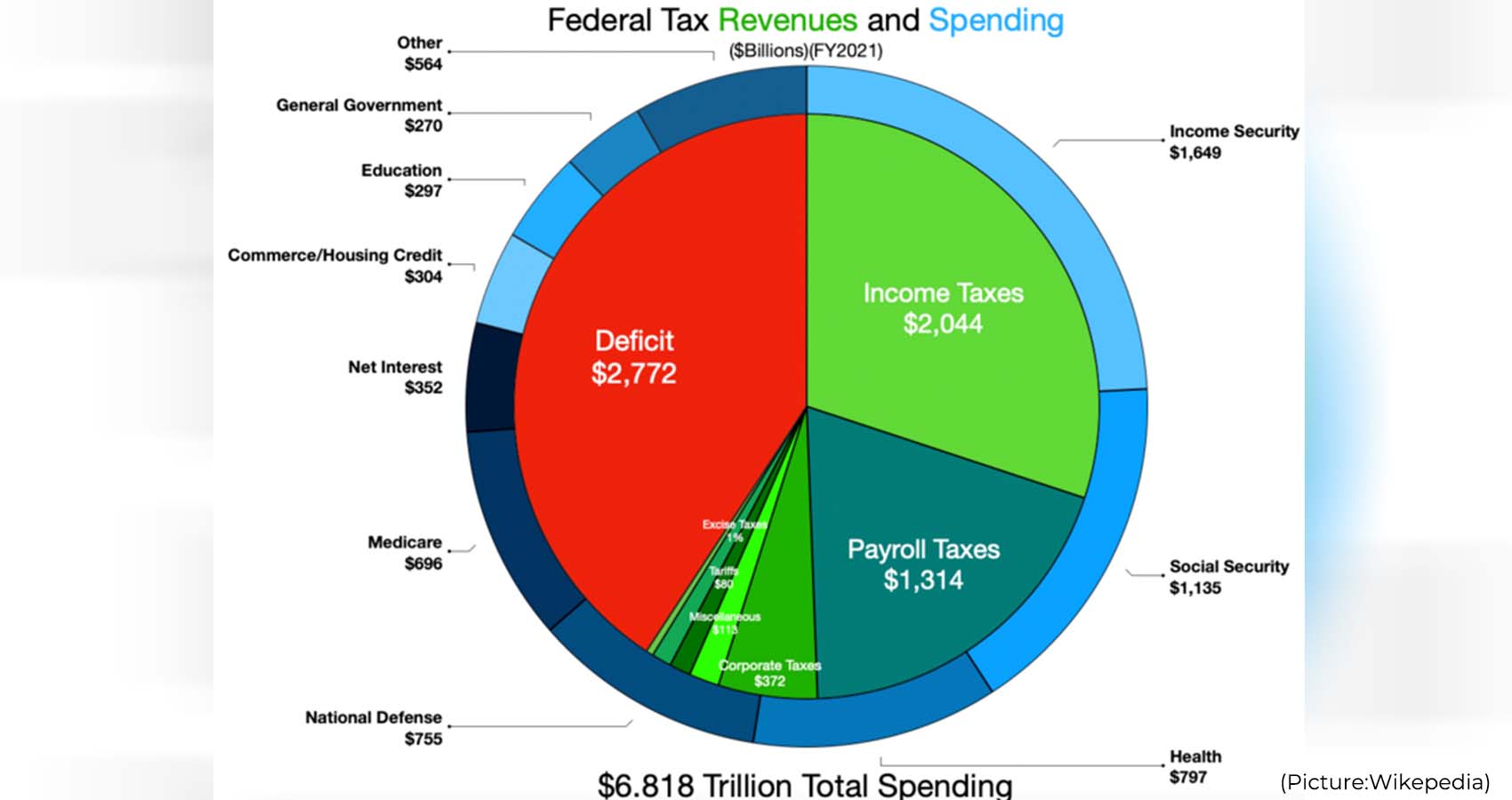
 Nonrevolving credit, such as student or car loans, grew by 8.4% to $3.4 trillion, also outpacing a smaller January gain.
Nonrevolving credit, such as student or car loans, grew by 8.4% to $3.4 trillion, also outpacing a smaller January gain.

 Withdrawal of major Western transnational companies – such as Shell, McDonald’s and Apple – will undoubtedly hurt many Russians – not only oligarchs, their ostensible target.
Withdrawal of major Western transnational companies – such as Shell, McDonald’s and Apple – will undoubtedly hurt many Russians – not only oligarchs, their ostensible target.

 Policymakers stress these are early days yet, and there is a lot that needs to be hammered out. All in all, the transactions conducted with digital dollars probably wouldn’t seem too different from existing private alternatives that allow us to pay for things by bringing our smartphones next to digital readers.
Policymakers stress these are early days yet, and there is a lot that needs to be hammered out. All in all, the transactions conducted with digital dollars probably wouldn’t seem too different from existing private alternatives that allow us to pay for things by bringing our smartphones next to digital readers.
 The report also noted that the Covid-19 pandemic has raised global income inequality, partly reversing the decline that was achieved over the previous two decades, Xinhua news agency reported.
The report also noted that the Covid-19 pandemic has raised global income inequality, partly reversing the decline that was achieved over the previous two decades, Xinhua news agency reported.

 “That is the way forward here,” said Ben Ritz, director of the Center for Funding America’s Future at the Progressive Policy Institute, who has advocated for a bill with fewer items. “Most of the party is starting to come around to that,” Ritz added. Some Democrats think their party made a mistake in going too large in the first place.
“That is the way forward here,” said Ben Ritz, director of the Center for Funding America’s Future at the Progressive Policy Institute, who has advocated for a bill with fewer items. “Most of the party is starting to come around to that,” Ritz added. Some Democrats think their party made a mistake in going too large in the first place.
 As we prepare for the return to repayment in May, we will continue to provide tools and supports to borrowers so they can enter into the repayment plan that is responsive to their financial situation, such as an income-driven repayment plan. Students and borrowers will always be at the center of our work at the Department, and we are committed to not only ensuring a smooth return to repayment, but also increasing accountability and stronger customer service from our loan servicers as borrowers prepare for repayment.”
As we prepare for the return to repayment in May, we will continue to provide tools and supports to borrowers so they can enter into the repayment plan that is responsive to their financial situation, such as an income-driven repayment plan. Students and borrowers will always be at the center of our work at the Department, and we are committed to not only ensuring a smooth return to repayment, but also increasing accountability and stronger customer service from our loan servicers as borrowers prepare for repayment.”
 Supply chain bottlenecks, with COVID-19-related worker absences at factories and ports still high, are also leading to low supplies and higher prices for consumer electronics, appliances and many other products.
Supply chain bottlenecks, with COVID-19-related worker absences at factories and ports still high, are also leading to low supplies and higher prices for consumer electronics, appliances and many other products.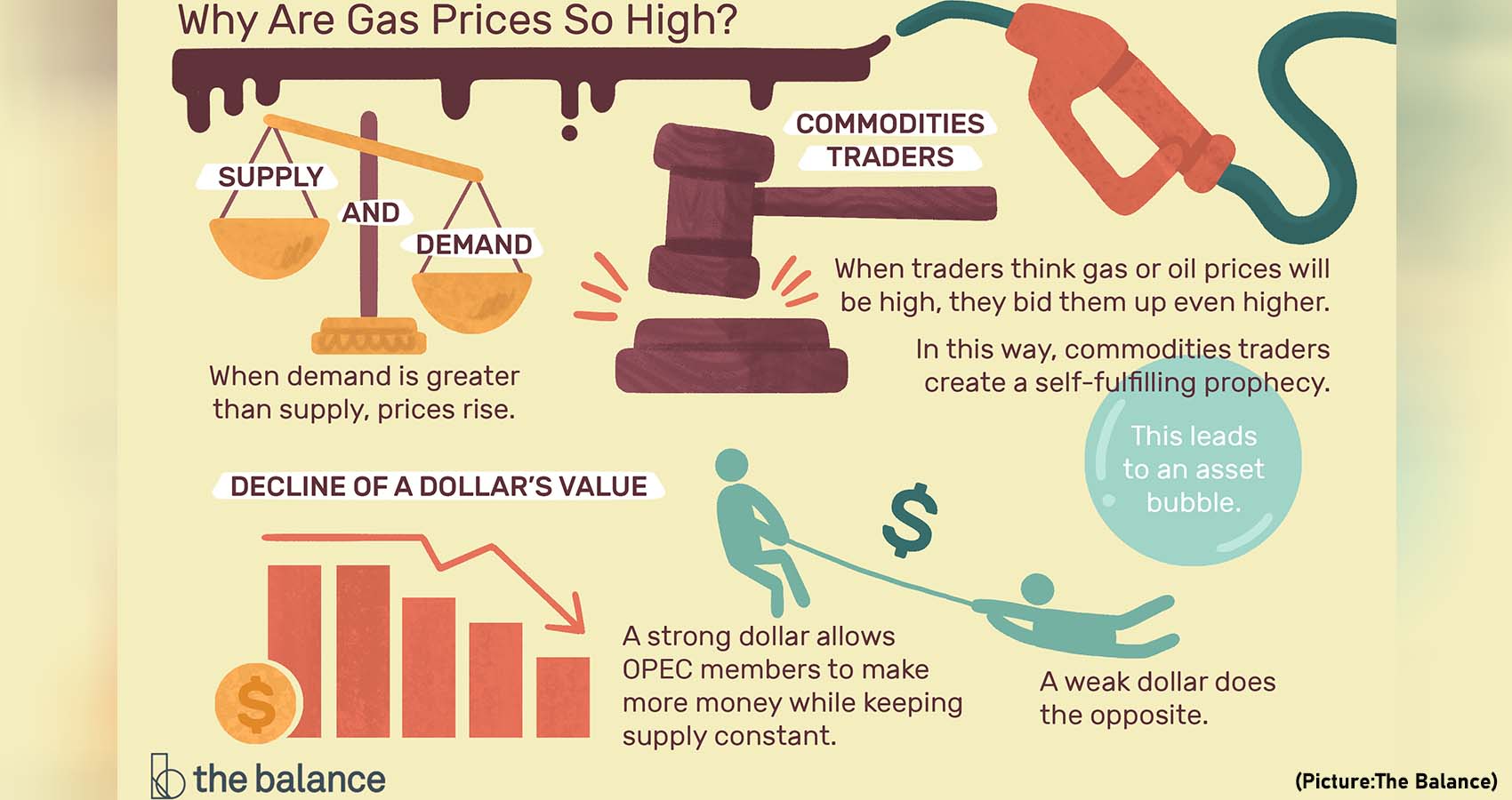
 Also, the volatility of gas prices means they can go down as sharply and as suddenly as they go up. In the spring of 2020, as the
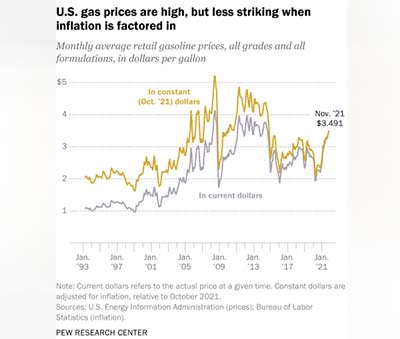
Also, the volatility of gas prices means they can go down as sharply and as suddenly as they go up. In the spring of 2020, as the  Where you buy gas also matters. Much of the U.S. petroleum industry is concentrated along the Gulf Coast, making it perhaps unsurprising that gas tends to be cheapest there. The average price in that region was $3.072 a gallon in late November, and in Texas it was also a hairsbreadth above $3.
Where you buy gas also matters. Much of the U.S. petroleum industry is concentrated along the Gulf Coast, making it perhaps unsurprising that gas tends to be cheapest there. The average price in that region was $3.072 a gallon in late November, and in Texas it was also a hairsbreadth above $3.
 The growing pools of cash are meant to entice young workers and hold on to existing staff at a time
The growing pools of cash are meant to entice young workers and hold on to existing staff at a time 
 But the CBDC is the official cryptocurrency issued by the Central Bank of India. This is the main difference between other cryptocurrencies and CDBC. The CBDC (Central Bank Digital Currency) will also be marketed through the blockchain technology as done by other virtual currencies . It is likely to be a digital token or electronic form of the current currency. The Reserve Bank of India will be in charge of supervising and monitoring the official crypto of the Indian government. Digital money cannot be withdrawn as we usually withdraw from banks and ATMs. Their transactions will be through digital platforms. It is not yet clear whether it will be listed on other crypto exchanges.
But the CBDC is the official cryptocurrency issued by the Central Bank of India. This is the main difference between other cryptocurrencies and CDBC. The CBDC (Central Bank Digital Currency) will also be marketed through the blockchain technology as done by other virtual currencies . It is likely to be a digital token or electronic form of the current currency. The Reserve Bank of India will be in charge of supervising and monitoring the official crypto of the Indian government. Digital money cannot be withdrawn as we usually withdraw from banks and ATMs. Their transactions will be through digital platforms. It is not yet clear whether it will be listed on other crypto exchanges.
 On honoring him his new crown, CM Stalin praised Rangaswami for his achievements in the US.
On honoring him his new crown, CM Stalin praised Rangaswami for his achievements in the US.

 India is followed by China, Mexico, the Philippines, and Egypt, the report said. In India, remittances are projected to grow 3% in 2022 to $89.6 billion, reflecting a drop in overall migrant stock, as a large proportion of returnees from the Arab countries await return, it said.
India is followed by China, Mexico, the Philippines, and Egypt, the report said. In India, remittances are projected to grow 3% in 2022 to $89.6 billion, reflecting a drop in overall migrant stock, as a large proportion of returnees from the Arab countries await return, it said.