Tax Day has recently passed and according to a recent Pew Research poll, Americans’ frustration with the tax code has reached its highest point in recent years. The majority of Americans, 56%, say they pay “more than their fair share” of taxes, with the number having increased from 51% from 2019.
It is also no surprise that almost two-thirds of Americans believe that the wealthy do not pay enough taxes, with 61% supporting the idea of raising taxes on households earning over $400,000. However, the definition of what constitutes a “fair share” of taxes is subjective and many Americans may not understand how much of the tax burden the rich bear.
In 2020, the top 1% of taxpayers paid $722 billion in income taxes, which accounted for 42.3% of all income taxes paid – the highest percentage in modern history. In contrast, the bottom 90% of taxpayers paid $450 billion in income taxes, or just 26.3% of the total, representing their lowest percentage of the tax burden in decades. This means that the top 1% of taxpayers pay a far greater share of the nation’s tax burden than 142 million of their neighbors combined.
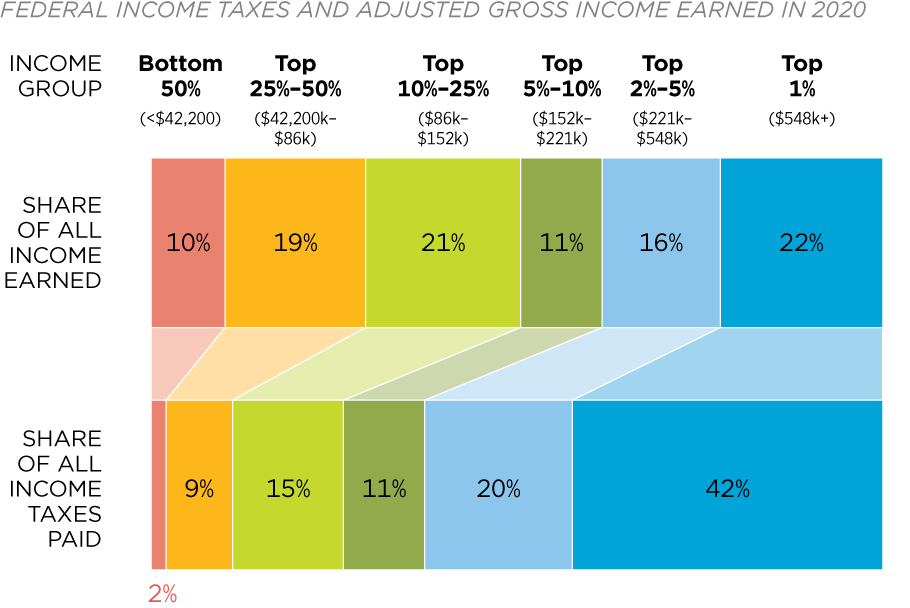
The wealthy do not pay a larger amount solely because they earn the most money. In 2020, the top 1% of taxpayers earned 22% of all adjusted gross income, while their 42.3% share of income taxes is nearly twice their income share. The opposite is true for the bottom 90%, who earned more than half of the nation’s income but paid only 26.3% of the taxes, representing roughly half of their share of the nation’s income. This was not the case in 1980, where the tax burden was more evenly shared. The bottom 90% earned 68% of the nation’s income and paid 52% of the income taxes, while the top 1% earned 9.6% of the nation’s income and paid 17% of the income taxes.
One of the reasons for the progressive tax system in the United States is the massive expansion of social programs delivered through the tax code over the past three decades. Many of the most significant programs aimed at lower-income families and those with children, such as the Child Tax Credit and the Earned Income Tax Credit, are run through the IRS, which deliver roughly $180 billion in benefits each year, much of which is refundable. Since the mid-1990s, tax credits have multiplied, with credits for adoption, child care, senior care, college tuition, buying electric cars or solar panels, and buying health insurance, among other things. However, these responsibilities are beyond the capacity of a tax collection agency, making it difficult for the IRS to function.
Record numbers of taxpayers now pay no income taxes after claiming their credits and deductions, with 34% of tax filers paying no income taxes due to generous credits and deductions in the tax code. In 2019, 54 million tax filers, equal to 34%, paid no income taxes because of the tax code’s generous credits and deductions. In 1980, only 21% of tax filers paid no income taxes due to credits and deductions.
Despite politicians’ rhetoric about ensuring the fair share of taxes, the burden on top earners continues to climb. If the wealthy were indeed able to use loopholes to avoid paying taxes, many of them would need better accountants.











