Close to the area I once called home lies one of India’s most dazzling shopping centers. During the day, the immense structure overshadows everything in its vicinity. At night, a dazzling array of lights starkly contrasts with the neighboring shops and houses, which have taken on a worn appearance from pollution and rain.
Within this grand establishment named Quest, residents of Kolkata with substantial disposable incomes indulge in luxury foreign brands like Gucci and dine at Michelin-starred restaurants.
However, life outside continues at a steady pace for individuals like my acquaintance, Amina.
She resides in a slum nestled in the shadow of Quest.
Amina embodies a statistic often mentioned yet rarely acknowledged: Approximately 60% of India’s nearly 1.3 billion inhabitants subsist on less than $3.10 per day, according to the World Bank’s median poverty line. Moreover, over 250 million people, constituting 21% of the population, survive on less than $2 per day.
Growing up as a middle-class Indian, I had limited exposure to the lives of the underprivileged. We inhabited distinct spheres, a divide that seemed to widen as India surged forward as a global economic force. While the affluent prospered, the impoverished largely remained in their dire circumstances, contributing to the expanding gap.
Presently, the wealthiest 10% in India command 80% of the nation’s wealth, as reported by Oxfam in 2017. Furthermore, the top 1% possesses 58% of the country’s wealth, in stark contrast to the United States, where the richest 1% owns 37% of the wealth.
Another illuminating perspective reveals that the wealth of 16 individuals in India equates to that of 600 million people.
These eye-opening statistics about my homeland evoke a sense of dichotomy. One facet of India showcases billionaires, technological advancements, nuclear capabilities, and democratic values. Conversely, there exists another India, inhabited by individuals like Amina, where nearly 75% of the population resides in villages, engaged in arduous labor; only 11% own refrigerators, and 35% lack basic literacy skills.
I am meeting Amina today because policymakers and journalists seldom engage with individuals like her to assess India’s progress. Quest Mall in Kolkata symbolizes India’s economic triumph, and I am curious to hear Amina’s perspective on it.
Amina and I go way back to 1998 when she began working at my parents’ residence. Each morning, she would trek from her dwelling about a mile and a half away, arriving around 10 AM to tend to household chores. Despite her age, which she claimed to be around 50 despite lacking any documentation, she exhibited remarkable resilience from years of domestic labor.
My mother held Amina in high regard, and even after my parents passed away in 2001 and I sold the flat, I made a point to visit Amina whenever I returned to Kolkata.
Over time, I learned about the challenges she faced, particularly after her husband’s passing, which left her struggling to secure steady employment due to her declining health. Despite my attempts to assist her financially, Amina insisted on earning her keep by offering services like massages or pedicures.
My frequent visits to India stem not only from my distinct upbringing but also from a deep fascination with the country’s evolution from a poverty-stricken former colony to a formidable global player.
I am mindful that Western perceptions of India often revolve around clichés such as corruption, traffic accidents, pollution, arranged marriages, and vibrant festivals. However, India’s societal landscape has evolved significantly, characterized by a burgeoning youth population, a surge in urban obesity rates, and the transformation of traditional trades due to the proliferation of the IT sector.
Such transformations necessitate constant reacquaintance with my birthplace.
Today, I am eager to reconnect with Amina and assess her well-being since our last encounter. Navigating through dim, labyrinthine alleys, I reach Amina’s modest dwelling. The air is thick with the aroma of cooking spices mingling with the acrid scent of coal-burning stoves.
Amina’s living conditions, reminiscent of those depicted in Katherine Boo’s “Beyond the Beautiful Forevers,” epitomize the struggles faced by individuals like her. Amidst scratched aluminum pots and an antiquated television set, Amina resides in a dimly lit room devoid of windows, paying a monthly rent equivalent to what she once earned at my parents’ residence.
Her room serves as a shared space for her and her grandchildren, offering a glimpse into the harsh realities endured by marginalized communities.
Economists like Devinder Sharma advocate for an alternative approach to India’s development, urging policymakers to address the systemic inequalities perpetuated by existing tax structures and government incentives that primarily benefit the affluent.
Conversely, Indian entrepreneurs attribute the widening wealth gap to systemic issues such as government corruption and inefficiency. Factors like gender, caste, and geographic location further exacerbate disparities, as highlighted by economic development expert Raj Desai.
As I engage with Amina in her humble abode, I am struck by her physical frailty, a stark contrast to her once robust demeanor. Despite her diminished mobility, Amina’s resilience remains evident as she eagerly anticipates our outing.
Accompanied by her granddaughter, Manisha, Amina ventures into an unfamiliar realm as we arrive at Quest Mall, where the dichotomy between old and new becomes palpable.
Outside the opulent mall, street vendors like Tapan Datta continue their daily routines, unfazed by the extravagant offerings within. However, our attempt to enter the mall is met with resistance from a vigilant security guard, underscoring the exclusivity of such establishments.
Inside, Amina’s astonishment at the immaculate surroundings is evident, offering a glimpse into a world previously beyond her reach. As we explore the mall, I observe the incongruity between the exorbitant price tags and Amina’s meager means, highlighting the stark disparities perpetuated by India’s economic growth.
While Amina’s inability to comprehend the astronomical prices provides a sense of relief, it also serves as a poignant reminder of the insurmountable barriers faced by individuals like her.
As we reflect on our experience, Amina’s poignant words resonate deeply, encapsulating the profound sense of resignation prevalent among marginalized communities.
Amidst academic discourse and policy debates surrounding India’s economic trajectory, Amina’s plight serves as a poignant reminder of the inherent inequities perpetuated by systemic injustices.
Despite the ongoing discourse regarding India’s economic future, the fundamental question of how to alleviate widespread poverty remains unanswered. While some advocate for progressive policies aimed at redistributing wealth, others emphasize the importance of addressing systemic issues such as education and healthcare.
As I bid farewell to Amina, her poignant words linger, serving as a testament to the enduring resilience of individuals like her amidst formidable challenges. In her world, devoid of the prospect of upward mobility, the American dream remains an elusive notion.
As I depart, I am reminded of the stark juxtaposition between luxury and deprivation, a sobering reality that underscores the urgent need for inclusive economic reforms aimed at uplifting the most vulnerable segments of society.




























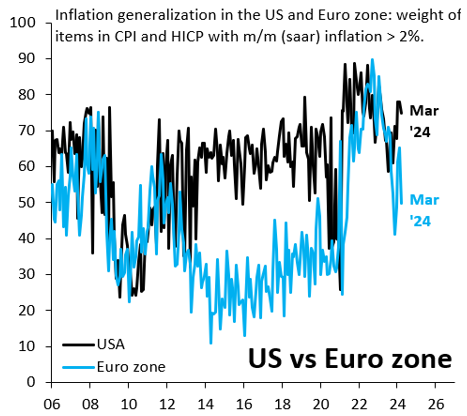
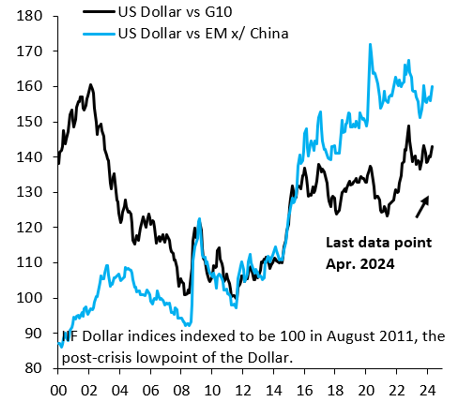
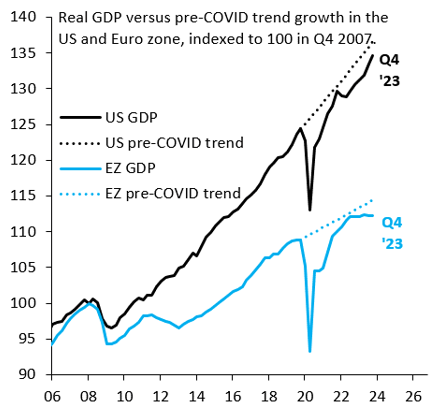 A stylized fact following the 2008 crisis is that U.S. growth substantially outperformed the rest of the advanced world. This again looks to be true in the aftermath of COVID-19 (Figure 1), with lots of debate on the underlying drivers. Some argue that this outperformance reflects loose fiscal policy and rapid immigration, while others see a productivity boom linked to tight labor markets. Whatever the source, cyclical outperformance may keep U.S. inflation stickier than elsewhere. There are some signs of this. Figure 2 shows the combined weight of items in the U.S. consumer price index (CPI) with month-over-month inflation above 2% (on a seasonally adjusted, annualized basis), alongside the same measure for the eurozone’s harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP). This metric is noisier than if we used year-over-year inflation, but it has the advantage of focusing on recent inflation dynamics, since there are no base effects to muddy the picture. Elevated inflation remains relatively broad-based in the U.S., consistent with strong growth, while inflation momentum is clearly fading in the eurozone.
A stylized fact following the 2008 crisis is that U.S. growth substantially outperformed the rest of the advanced world. This again looks to be true in the aftermath of COVID-19 (Figure 1), with lots of debate on the underlying drivers. Some argue that this outperformance reflects loose fiscal policy and rapid immigration, while others see a productivity boom linked to tight labor markets. Whatever the source, cyclical outperformance may keep U.S. inflation stickier than elsewhere. There are some signs of this. Figure 2 shows the combined weight of items in the U.S. consumer price index (CPI) with month-over-month inflation above 2% (on a seasonally adjusted, annualized basis), alongside the same measure for the eurozone’s harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP). This metric is noisier than if we used year-over-year inflation, but it has the advantage of focusing on recent inflation dynamics, since there are no base effects to muddy the picture. Elevated inflation remains relatively broad-based in the U.S., consistent with strong growth, while inflation momentum is clearly fading in the eurozone.