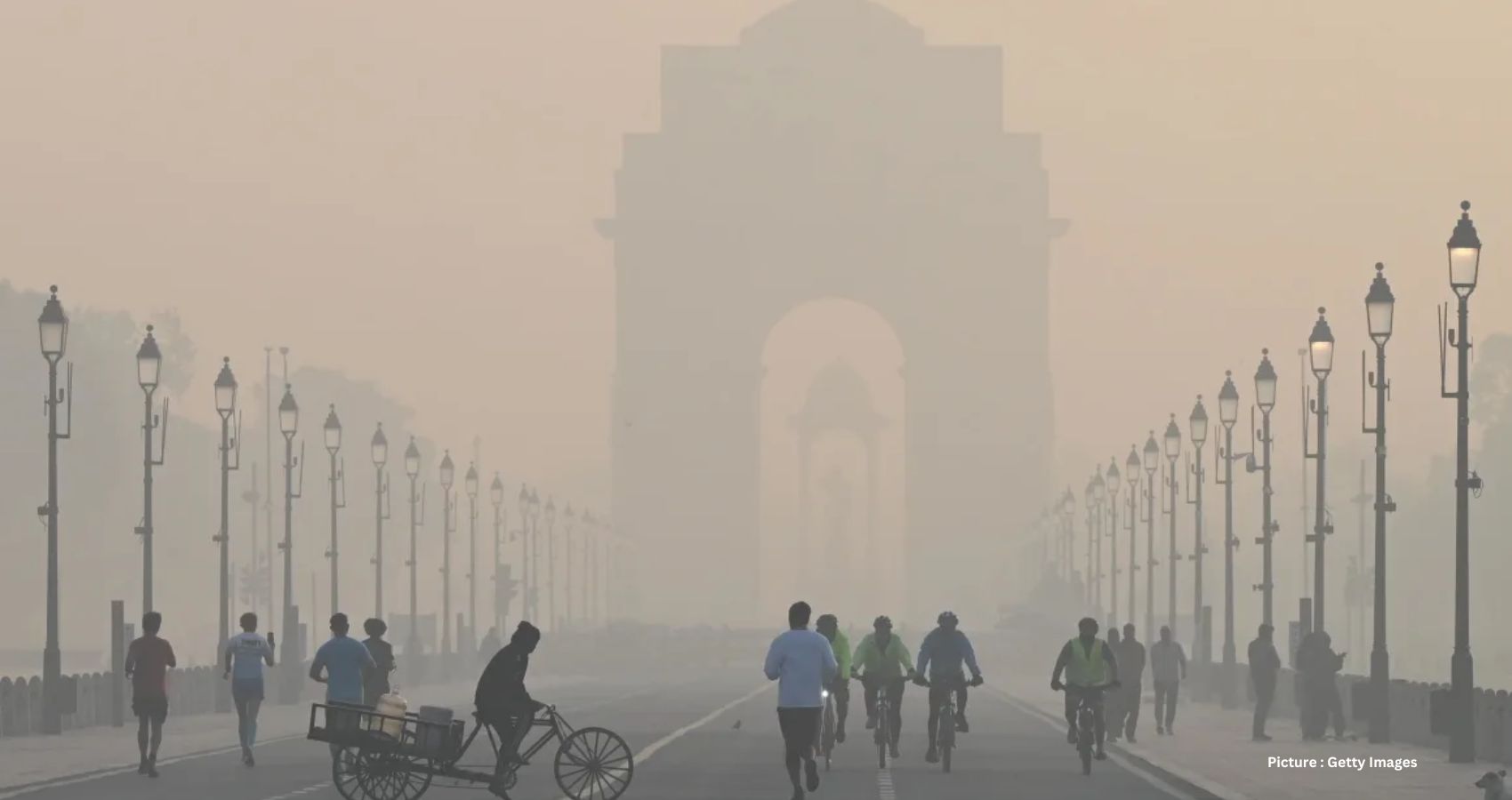
A recent report has shed light on the alarming state of air pollution worldwide, particularly in Asia. The findings reveal that of the 100 cities grappling with the worst air quality, almost all were located in Asia, indicating a profound crisis that imperils the health of billions of individuals globally.
The report, conducted by IQAir, an organization dedicated to tracking air quality on a global scale, underscores the severity of the situation. It discloses that a staggering 83 out of these 100 cities were situated in India alone, surpassing the air quality guidelines set by the World Health Organization (WHO) by more than tenfold.
Specifically focusing on the presence of fine particulate matter known as PM2.5, the study highlights its pervasive and hazardous nature. PM2.5, originating from various sources such as the combustion of fossil fuels, dust storms, and wildfires, poses severe health risks upon inhalation, penetrating deep into lung tissue and even entering the bloodstream. The consequences include a heightened susceptibility to asthma, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and cognitive impairments, particularly in children.
Frank Hammes, the CEO of IQAir Global, emphasizes the far-reaching impacts of air pollution on human lives, stating, “We see that in every part of our lives that air pollution has an impact.” He notes that in heavily polluted countries, individuals may be losing up to six years of their lives due to air pollution-related ailments, highlighting the urgent need for improved air quality.
India, in particular, faces a dire situation, with cities like Begusarai in Bihar state ranking as the most polluted globally, with PM2.5 concentrations exceeding WHO guidelines by 23 times. Across the country, a staggering 1.3 billion people, constituting 96% of the population, are exposed to air quality levels far surpassing WHO recommendations.
The report identifies Central and South Asia as the worst-performing regions globally, with countries like Bangladesh, Pakistan, India, and Tajikistan ranking among the most polluted. Notably, South Asia stands out, with nearly all of the 30 most polluted cities located in India, Pakistan, or Bangladesh.
Addressing the root causes of this crisis, Hammes emphasizes the necessity for significant changes in energy infrastructure and agricultural practices to mitigate pollution levels effectively. He also underscores the interconnectedness of outdoor and indoor air pollution, stressing that actions like cooking with dirty fuel exacerbate indoor air quality issues.
The report’s global analysis reveals a bleak reality, with a staggering 92.5% of locations worldwide exceeding WHO’s PM2.5 guidelines. Only a handful of countries and territories, including Finland, Estonia, and New Zealand, boast healthy air quality levels.
Tragically, air pollution-related health issues claim millions of lives annually. The burning of fossil fuels alone leads to the premature deaths of 5.1 million individuals annually, while combined ambient and household air pollution accounts for 6.7 million deaths yearly, according to WHO.
The report underscores the pivotal role of the climate crisis in exacerbating air pollution levels globally. Changing weather patterns, intensified wildfires, and prolonged pollen seasons contribute to worsening air quality, with vulnerable communities bearing the brunt of these environmental shifts.
While North America grapples with the aftermath of devastating wildfires, Asia experiences a resurgence in pollution levels, with China witnessing a reversal in declining pollution trends. Despite previous efforts to curb pollution, Chinese cities experienced a resurgence in smog, underscoring the challenges in sustaining clean air initiatives.
Southeast Asia also faces escalating pollution levels, with Indonesia, Vietnam, and Thailand registering significant increases. Thailand, in particular, grapples with toxic smog, prompting authorities to implement measures such as remote work arrangements to mitigate health risks.
However, amidst these dire circumstances, there are glimmers of hope. The report highlights growing civic engagement and pressure from various stakeholders to monitor and address air quality issues, signaling a promising shift towards prioritizing environmental health.
As Frank Hammes aptly summarizes, “Ultimately that’s great because it really shows governments that people do care.” This collective effort is crucial in driving meaningful change and safeguarding the health and well-being of communities worldwide.