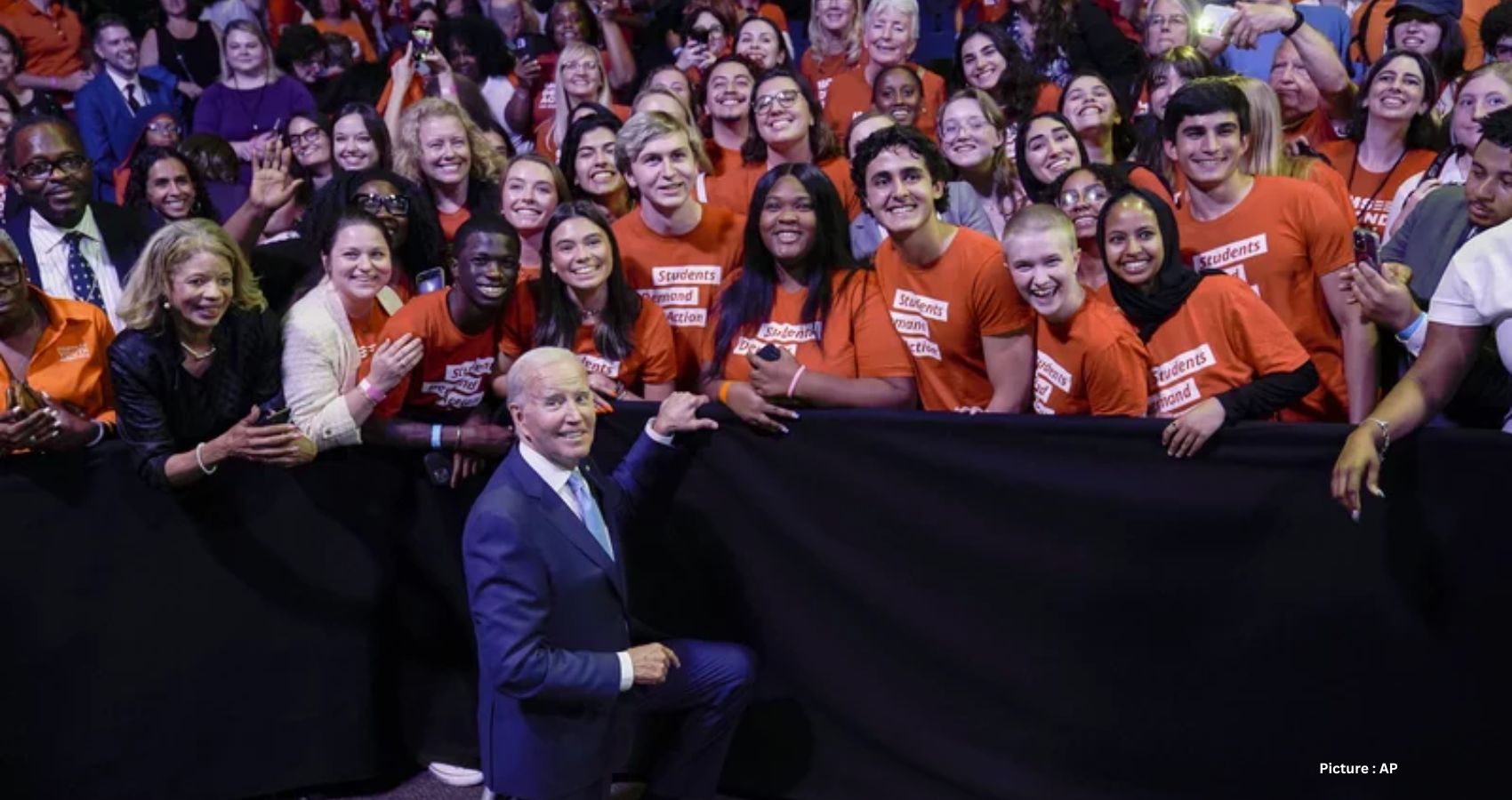President Biden’s reelection campaign is embarking on a new endeavor, introducing a fresh initiative aimed at connecting with young Americans as the general election approaches. The campaign is rolling out Students for Biden-Harris, a program centered on assembling a substantial volunteer base of youthful supporters through various student-led organizations across the country. This move coincides with the potential pivotal role that Gen Z and younger millennials, individuals under 30, might play in the upcoming 2024 presidential race.
Eve Levenson, the Director of Youth Engagement for the campaign, emphasized the significance of this initiative, stating, “This is the primary way for a student to get involved right now,” as reported by NPR. Students for Biden-Harris marks the formal commencement of a youth outreach strategy spearheaded by Levenson. The launch initiates a vigorous recruitment drive for volunteers, with subsequent plans to aid students in establishing chapters or presence in their high schools and colleges, fostering collaboration with these volunteers throughout the electoral cycle.
The campaign is pursuing multiple avenues to engage with young people in anticipation of the election. Among these efforts is “relational organizing,” where volunteers are equipped with campaign materials to directly reach out to individuals in their communities. This approach will be integral to both Students for Biden-Harris and other endeavors targeting young people beyond college campuses.
Furthermore, the announcement follows closely on the heels of the Biden campaign’s recent launch of an affiliated TikTok account, a move perceived as a nod to the app’s popularity among younger Americans. Despite this outreach, the White House is advocating for legislation that would effectively ban TikTok under its current ownership by the Chinese company ByteDance.
While Gen Z and younger millennials largely supported Biden in 2020, securing their support in the upcoming election isn’t assured. According to the latest Harvard Youth Poll, voters under 30 are displaying diminished enthusiasm compared to four years ago. Despite substantial turnout in recent major elections, this demographic remains divided in their support for Biden, particularly in light of criticisms regarding his handling of issues like the conflict in Gaza and emerging movements advocating for ‘Uncommitted’ votes in the Democratic primary.
Acknowledging these concerns, the campaign underscores that the youth vote isn’t monolithic, with no single issue defining it. Highlighting other areas of importance to young voters, such as safeguarding abortion access and the administration’s efforts to address climate change and student loan forgiveness, the campaign aims to bridge information gaps.
Levenson emphasizes the need to address these informational deficits, stating, “Young people have fought for so many things and so much has gotten done. People don’t necessarily know what it is that’s gotten done.”
The launch of Students for Biden-Harris coincides with Biden receiving endorsements from numerous organizations focused on young voters, including Voters of Tomorrow, NextGen PAC, and Planned Parenthood Action Fund. However, recent demands from progressive organizations emphasizing the necessity for bolder action from the president indicate ongoing pressure. In a letter issued ahead of Biden’s State of the Union address, these organizations outlined a “Finish the Job Agenda,” urging Biden to declare a lasting ceasefire in Gaza and championing a progressive agenda that resonates with younger generations.
“Going into 2024, you must run on a bold and progressive agenda that invests in our generation and recognizes the need for immediate action to combat the issues of our time,” the letter emphasized, urging Biden to demonstrate unwavering commitment to the concerns of younger voters.