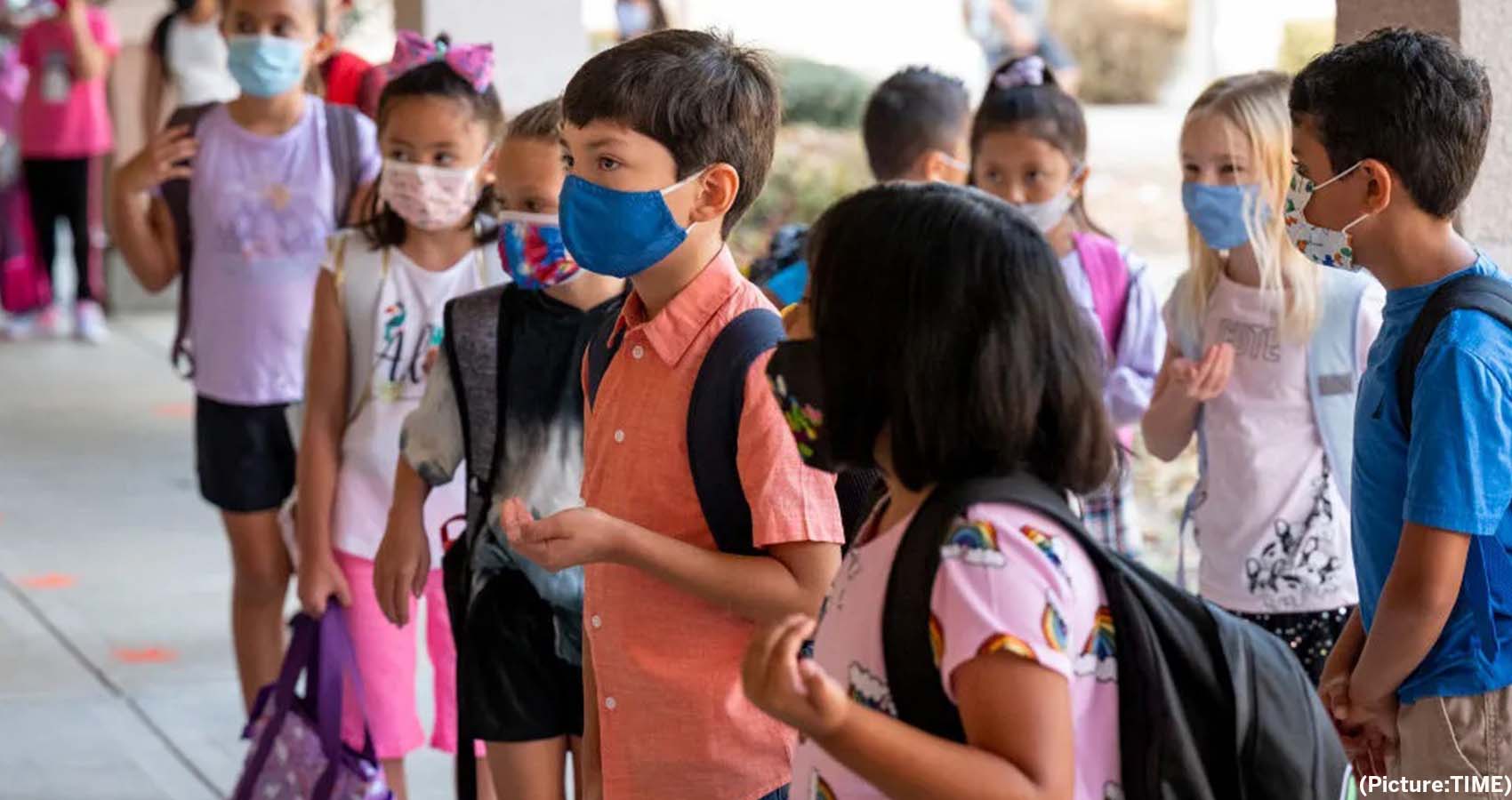
In a step many parents have been awaiting, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) this afternoon granted emergency-use authorization to Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine for children ages 5 to 11.
After reviewing evidence provided by Pfizer and taking into account the overwhelmingly positive recommendation of the agency’s independent advisory panel, FDA officials said the shot’s benefits outweigh its potential risks for young kids. It has been shown to be more than 90% effective at preventing symptomatic disease among kids 5 to 11, with no serious side effects reported among a group of 3,000 children who participated in trials.
 Like Pfizer-BioNTech’s adult vaccine, the pediatric version is meant to be given in two doses, spaced three weeks apart. Each dose, however, is smaller than that given to adults.
Like Pfizer-BioNTech’s adult vaccine, the pediatric version is meant to be given in two doses, spaced three weeks apart. Each dose, however, is smaller than that given to adults.
The shot must still be recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) before it is widely available to younger kids, but the FDA’s green light is a major step toward that outcome. The CDC’s advisory committee will meet to discuss the shot next week.
If the CDC does recommend the shot for some or all 5- to 11-year-olds, the next challenge will be convincing parents to get it for their children. In a recent poll, almost 30% of U.S. parents with kids in that age group said they would vaccinate them right away, but another 35% said they either definitely wouldn’t vaccinate or wouldn’t unless required. The remaining chunk said they wanted to “wait and see.”
Waiting to vaccinate all children would be a mistake. Based on the data we have, the right answer is clear: the CDC should recommend that all kids ages five to eleven should have be vaccinated as quickly as possible.
There is one thing all experts agree on: Vaccinating children should be based on rigorous evidence and we should set a particularly high bar for using vaccines in healthy children.
The Pfizer COVID vaccine has cleared that bar. Whether these vaccines work in kids is beyond dispute: they are extremely effective, reducing COVID infections by more than 90 percent. This number is based on data gathered during the Delta surge in the U.S., when vaccine breakthroughs among adults were becoming more common in the U.S. Such a high level of protection from the vaccine at a time when infection rates were extremely high is remarkable.
The next question is how the risks and benefits of the vaccine compare to the risks of getting COVID. Here, the calculation is also straightforward: the virus is a constant threat, to our children and all with whom they interact—including playmates, friends, and relatives. We have seen what COVID can do if we don’t control its spread. The worst of the Delta surge is behind us, but over 1000 Americans still die every day from the disease. Vaccines prevent infections and the spread of the virus, and save lives.
Like all vaccines, COVID vaccines can have the standard side-effects of a sore arm, fever or headaches, but these side-effects are mild and short-lived. There are also important concerns about one specific side effect that is crucial to recognize and fully understand: myocarditis—or an inflammation of the heart muscle.
There is a need to start preparing for a world in which SARS-CoV2 will be endemic, circulating for decades or longer, just like measles, whooping cough and the flu. This is why essentially every expert on child health has come out in support of vaccinations. The American Association of Pediatrics, has been vocally supportive, as has the American Association of Family Practitioners, who represent physicians who care for millions of children.
It is helpful to take a step back, and remember how vaccines have transformed our lives, and the life expectancy of our children. We give children dozens of vaccines, without which they would be vulnerable to potentially fatal diseases from measles to pneumococcal disease—diseases that continue to sicken unvaccinated children around the world. It is time for the CDC to continue its important work on protecting our children by adding another tool to the arsenal. We need COVID vaccinations for all children five to eleven years old so parents can get their children vaccinated and keep them safe. That’s what I’m going to do.
Where children are being vaccinated
Cuba became the first country in the world to vaccinate children as young as 2 last month, with the government saying that its homegrown vaccines are safe for younger kids. Cuba has yet to provide data on its vaccines to outside observers, but has said it will seek WHO approval.
Chile, China, El Salvador and the UAE have also approved vaccines for younger children. In Chile, children aged 6 and older can get the Sinovac shot, while in China, the Sinovac and CoronaVac vaccines are authorised for use in children as young as 3. In El Salvador, children as young as 6 will soon be able to get vaccinated, while in the UAE — where Sinopharm is approved for 3-year-olds — the government has made it clear that the vaccination program will be optional. Meanwhile, US children between 5 and 11 are now eligible for the vaccine starting this fall, after approval came from the USFDA.
Still weighing the option
The UK has been more cautious than many other European countries in regard to vaccinating younger populations, only recommending the shot for 12-15 year olds, following advice from its chief medical officers.
France, Denmark, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Spain and Poland are among EU countries that have rolled out their vaccination campaigns for 12-15 year olds, with uptake varying across the bloc. Switzerland — which is not part of the EU — has been vaccinating the younger age group since June. Sweden will offer the vaccine to 12-15 year-olds later in the fall.
And India?
If approved by India’s drugs regulator, Covaxin would be the first shot to be available for kids aged between 2 and 12, while those in the 12-18 years age-group can choose between Covaxin and Zydus Cadila’s DNA-based vaccine. Two other companies, Serum Institute of India and homegrown drugmaker Biological E, have also been allowed to test their shots on children.