Pope Francis has frequently spoken about climate change during his decadelong leadership of the Roman Catholic Church. In 2015, he devoted an entire encyclical to the matter, citing scientific consensus that the Earth is warming due to human activity. He predicted “serious consequences for all of us” if current trends continue.
Despite Francis’ outspokenness on the subject, not all Catholics in the United States share his concerns, and their views vary by political affiliation, race and ethnicity, and age.
How we did this
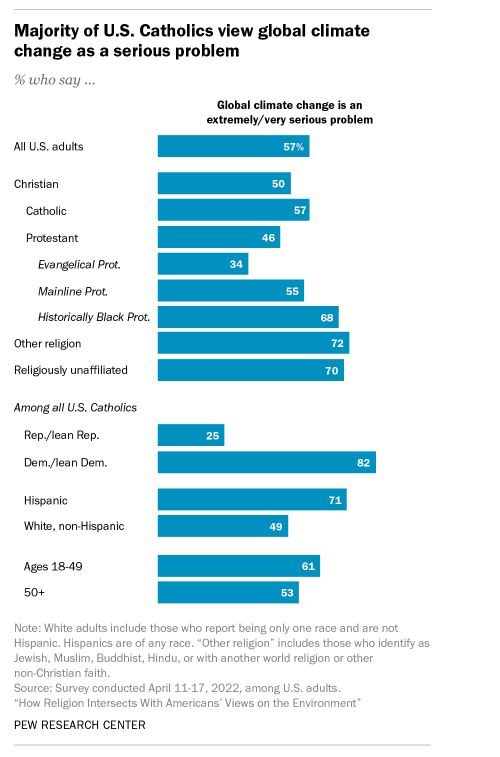
While 82% of Catholics who are Democrats or lean toward the Democratic Party say global climate change is an extremely or very serious problem, just a quarter of Republican or Republican-leaning Catholics say the same, according to a 2022 Pew Research Center survey.
When it comes to race and ethnicity, 71% of Hispanic Catholics see climate change as an extremely or very serious problem, compared with 49% of White, non-Hispanic Catholics. (There were not enough Black or Asian Catholics in the 2022 survey to analyze separately.)
In addition, Catholics ages 18 to 49 are somewhat more likely than Catholics ages 50 and older to express a high level of concern about climate change (61% vs. 53%).
Broadly speaking, Catholics are no more likely than Americans overall to view climate change as a serious problem. An identical share in each group say global climate change is either an extremely or very serious problem (57%).
But views among Catholics differ, reflecting similar splits in the wider U.S. population. U.S. adults who are 49 or younger, Democratic, or identify as a race or ethnicity other than non-Hispanic White are generally more likely than those who are 50 or older, Republican, or White to express concern about climate change.
Among U.S. adults overall, opinion about climate change is strongly tied to political partisanship. Democrats and Democratic leaners are far more likely than Republicans and Republican leaners to say that global climate change is an extremely or very serious problem (83% vs. 25%). This gap underlies much of the apparent differences in views among religious groups, including Catholics. Generally speaking, U.S. Catholics are politically evenly divided. But Catholics who are White or older are far more likely than those who are Hispanic or younger to be Republican.
Partisan and demographic differences in Catholics’ views of climate change extend to other environment-related topics, too. For example, just over half of Catholics (54%) say the Earth is warming mostly due to human activity – in line with the pope’s stance. A quarter say it is mostly warming due to natural patterns, while 9% say there is no solid evidence the planet is getting warmer. Catholics who are Democratic, younger or Hispanic are far more likely than those who are Republican, older or White to say the Earth is mostly warming due to human activity.
In addition to asking Americans about their own views on climate change, the 2022 Center survey asked respondents how much they hear about the topic in sermons.
Among those who attend religious services at least monthly, U.S. Catholics indicate that climate change is not discussed frequently from the pulpit. About one-in-ten (8%) say there is a great deal or quite a bit of discussion on climate change in sermons, while 50% say there is either some or a little discussion of it. About four-in-ten (41%) regular Mass attenders say there is no discussion of climate change.
Overall, 58% of Catholic service attenders say there is at least a little discussion of climate change in sermons, similar to the share of mainline Protestant attenders (62%), and much higher than the share of evangelical Protestant attenders who report this (40%).
Among Catholics who attend Mass at least monthly, 36% say they have heard at least a little about climate change in sermons and that those sermons always or often express the view that “we have a duty to care for God’s creation.” Smaller shares say sermons at their congregation always or often express “support for actions to limit the effects of climate change” (23%); “concern that policies aimed at reducing climate change give too much power to the government” (9%); or “the view that we don’t need to worry about climate change” (8%).



