India is set to become the world’s most populous country next year, overtaking China with its 1.4bn people, according to UN figures. On World Population Day, the United Nations has released a report projecting India to surpass China as the world’s most populous country next year. It further stated that the world population is forecast to reach eight billion by mid-November 2022.
 By this November, the planet will be home to 8 Billion people. That overall population milestone “is a reminder of our shared responsibility to care for our planet and a moment to reflect on where we still fall short of our commitments to one another,” Secretary General Antonio Guterres said, without citing specifics.
By this November, the planet will be home to 8 Billion people. That overall population milestone “is a reminder of our shared responsibility to care for our planet and a moment to reflect on where we still fall short of our commitments to one another,” Secretary General Antonio Guterres said, without citing specifics.
“This is an occasion to celebrate our diversity, recognize our common humanity, and marvel at advancements in health that have extended lifespans and dramatically reduced maternal and child mortality rates,” he added.
But population growth is not as rapid as it used to be. It is now at its slowest rate since 1950 and is set to peak, says the UN, around the 2080s at about 10.4bn though some demographers believe that could happen even sooner.
Currently, with 4.7 billion Asia is the most populous continent and has 61 per cent of the global population,17 per cent reside in Africa (1.3 billion), 10 per cent in Europe (750 million), 8 per cent in Latin America and the Caribbean (650 million), and the remaining 5 per cent in Northern America (370 million) and Oceania (43 million).
According to World Population Prospects 2019, China with a 1.44 billion population and India with 1.39 billion are the two most populous countries in the world, representing 19 and 18 per cent of the world’s population, respectively. However, by around 2023, India’s population will overtake China to become the most populous country with China’s population projected to decrease by 31.4 million, or around 2.2 per cent, between 2019 and 2050.But the population of the world is expanding unevenly.
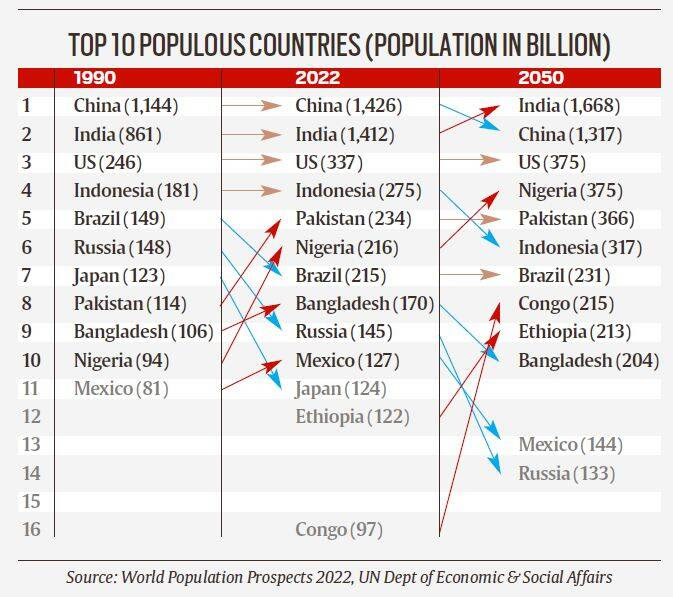 More than half the growth we will see in the next 30 years will happen in just eight countries – the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and Tanzania.
More than half the growth we will see in the next 30 years will happen in just eight countries – the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and Tanzania.
At the same time, some of the world’s most developed economies are already seeing population decline as fertility rates fall below 2.1 children per woman, which is known as the “replacement rate”. In 61 countries, the report says, populations will decline by at least 1% by 2050.
With one of the lowest fertility rates in the world (at 1.15 children per woman), China has announced that its population is due to start declining next year – much earlier than previously thought. That is despite the country abandoning its one child policy in 2016 and introducing incentives for couples to have two or more children.
As India’s population continues to grow it will almost certainly overtake China as the country with the biggest population in the world.
Fertility rates are falling globally – even in many of the countries where the population is expanding. That is because, as previous generations expand, there are more people having children, even if individually those people are having fewer children than their parents did.
Growth is also largely thanks to developments in medicine and science which mean that more children are surviving into adulthood and more adults into old age. That pattern is likely to continue, which means that by 2050 the global average life expectancy will be around 77.2 years.
But this pattern means that the share of the global population aged 65 years or above is projected to rise from 10% this year to 16% in 2050. Again the distribution will be unequal with some countries, in East Asia and Western Europe, already seeing more extremes in ageing.
