Experts discuss valerian root, often dubbed “nature’s Valium,” highlighting its potential benefits for sleep and anxiety while cautioning against misleading comparisons to the prescription sedative.
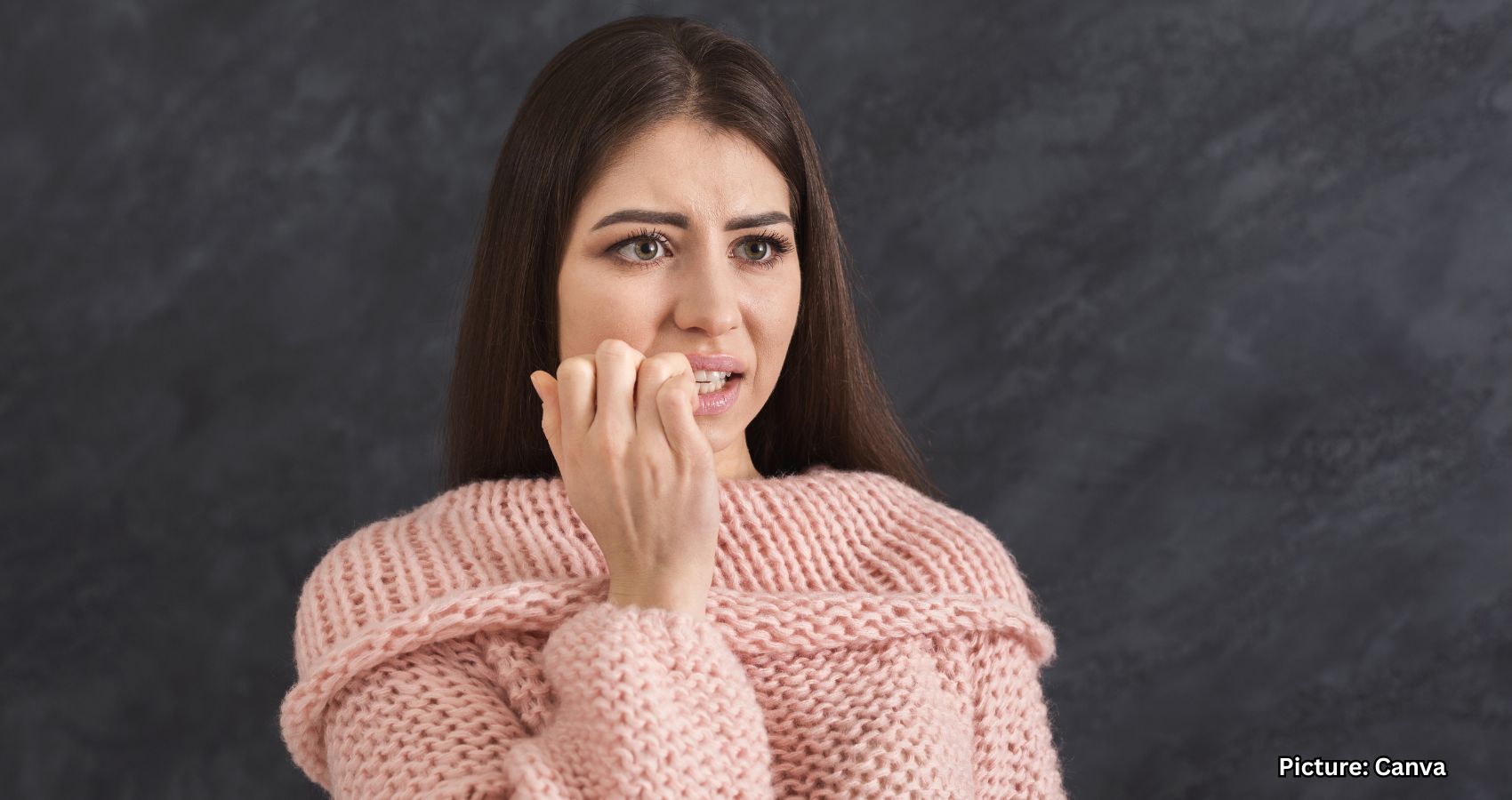
Valerian root, an herbal supplement known for its calming properties, has gained popularity as “nature’s Valium.” However, experts express caution regarding this comparison, suggesting it may mislead users about the herb’s effectiveness and safety.
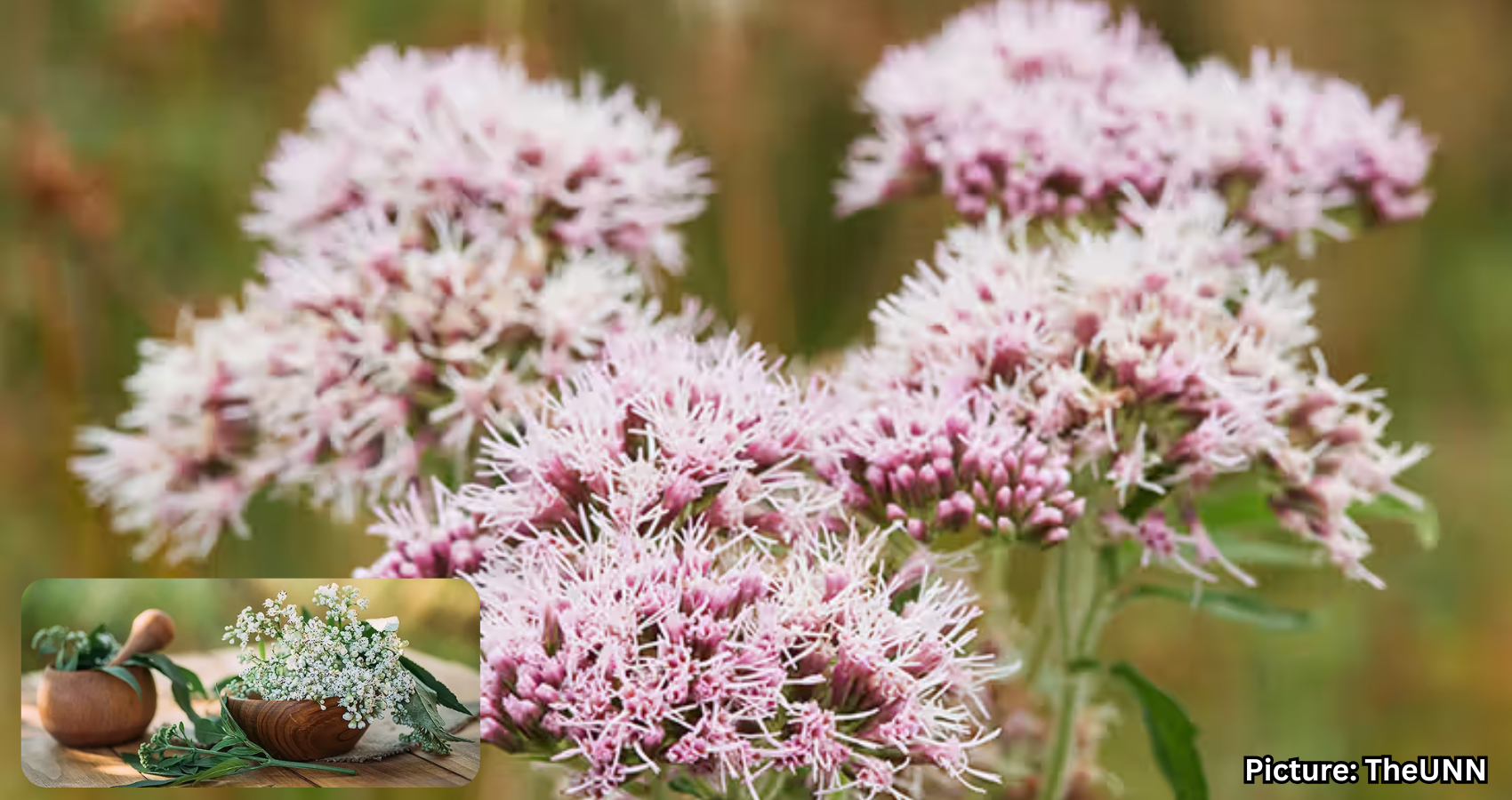
Valerian, derived from the roots of the Valeriana officinalis plant, has been used for centuries to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. This flowering plant is native to Europe and Asia but has also become established in parts of northeastern America, according to the American Botanical Council (ABC).
The herb has a long history of medicinal use, primarily aimed at alleviating anxiety and stress, as well as enhancing sleep. Historically, valerian has also been utilized for treating migraines, fatigue, and stomach cramps. It can be consumed in various forms, including teas, tinctures, capsules, and tablets, as noted by the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Despite its widespread use, the NIH points out that research on valerian’s efficacy is relatively limited. However, some clinical trials have investigated its effects. Stefan Gafner, Ph.D., chief science officer of the American Botanical Council, noted that a 2020 review published in the Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine found both powdered root and root extracts to provide a “clear” benefit in treating anxiety.
Gafner emphasized that valerian could be a “safe and effective herb to promote sleep and prevent associated disorders.” However, he cautioned against equating valerian with diazepam, the active ingredient in Valium. “While both are used to relieve anxiety, valerian is a much milder ingredient, primarily suited for mild cases of anxiety and sleep issues,” he explained.
Unlike valerian, diazepam carries a risk of dependence and is typically prescribed for short-term use. The potential adverse effects associated with diazepam are also significantly different from those of valerian. Gafner expressed his support for valerian root as a remedy for anxiety and stress, stating, “I have used it myself and believe it’s an ingredient with well-documented benefits, especially for people with problems falling asleep.” He added that valerian is generally well-tolerated but advised caution when operating heavy machinery or driving after use.
Dr. Joseph Mercola, a board-certified family medicine physician and author, also weighed in on the topic. He cautioned that the comparisons between valerian and Valium may “exaggerate what the science actually shows.” Mercola explained that valerian root contains compounds that may enhance calming brain chemicals, particularly the neurotransmitter GABA, which helps to reduce nerve activity and promote relaxation.
While some studies indicate modest improvements in sleep quality or reduced time to fall asleep, others have found no significant difference compared to a placebo. Mercola highlighted potential side effects of valerian, including headaches, dizziness, digestive upset, and next-day grogginess. He advised against using valerian as a primary strategy for managing anxiety, stress, or sleep issues.
Mercola emphasized the importance of addressing the underlying causes of poor sleep rather than relying solely on herbal sedatives. “When you fix those foundations, you often find that you no longer need an herbal sedative at all,” he stated. He recommended lifestyle changes, such as exposure to bright sunlight during the day to regulate circadian rhythms and promote melatonin production at night.
Additionally, Mercola suggested that complete darkness at night supports the hormonal signals necessary for deep, restorative sleep. He also noted that certain nutrients, such as magnesium, can help regulate the nervous system and promote relaxation.
In conclusion, while valerian root may offer some benefits for sleep and anxiety, experts urge caution in its use and advise individuals to consider a holistic approach to improving sleep quality. By focusing on lifestyle adjustments and addressing the root causes of sleep disturbances, individuals may find more effective and sustainable solutions.
Fox News Digital reached out to valerian root manufacturers for comment on this topic.
According to Fox News Digital, the discussion surrounding valerian root highlights the need for careful consideration when exploring herbal remedies for anxiety and sleep issues.