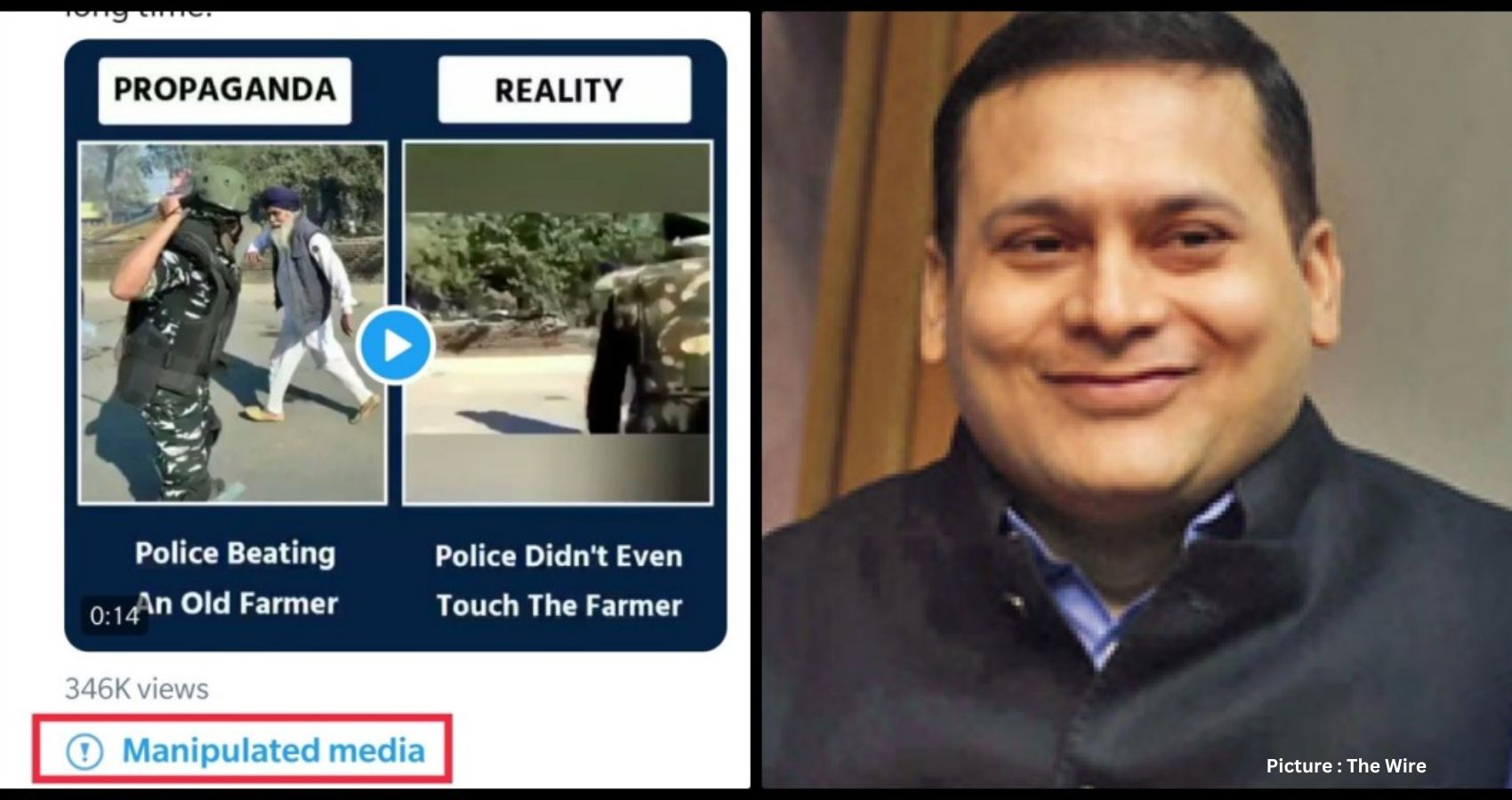
In a notable turn of events, Twitter took action against Amit Malviya, the head of the Bharatiya Janata Party’s IT cell, by tagging one of his tweets as ‘manipulated media’. This marks a significant departure as it’s the first instance of Twitter applying restrictive measures against a prominent Indian political figure.
This move comes in the wake of Twitter’s recent policy adjustments aimed at curbing the dissemination of misinformation on its platform. One of the key changes introduced by Twitter is its heightened vigilance towards manipulated media, a policy that was initially outlined in November 2019.
The genesis of this policy can be traced back to Twitter’s recognition of the need to address a broader spectrum of deceptive media practices compared to its counterparts like Facebook. While Facebook primarily focused on combatting deepfakes—videos synthesized from scratch—Twitter’s approach was more encompassing. It took into account user feedback indicating a preference for contextualization over outright removal of manipulated media.
The precedent for such actions was set when Twitter flagged a video posted by then-US President Donald Trump in June 2020. Trump’s tweet featured a clip portraying two toddlers of different races hugging, with a CNN-like chyron falsely insinuating racism. This manipulation was promptly identified by journalists, who clarified that the original story was about the friendship between the children.
In contrast, the tweet by Malviya didn’t involve doctored media but rather an edited clip designed to distort reality. The edited footage, in response to a widely circulated image showing a policeman seemingly striking an elderly farmer during protests, was used by Malviya to propagate a narrative suggesting that the baton didn’t actually make contact with the farmer. Moreover, Malviya dismissed accusations of government violence against peaceful protesters as opposition propaganda.
However, a closer examination of the events, as elucidated by an Alt News article, reveals instances of police resorting to lathi charges against farmers, who retaliated with stone-pelting. Various news outlets reporting from the scene corroborated this, depicting scenes of violent police action in response to farmers breaking blockades.
Twitter’s decision to flag Malviya’s tweet as ‘manipulated media’ hinges on its policy’s emphasis on preventing deceptive usage of media content. The platform’s Synthetic and Manipulated Media policy stipulates that sharing media in a manner intended to mislead or deceive, thereby fostering confusion or misunderstanding, warrants intervention.
While Twitter’s efforts to hold political leaders accountable for misleading content have garnered praise, questions linger regarding the consistency of its application. Internationally, the last instance of Twitter invoking its ‘synthesized or manipulated media’ clause against political figures dates back to September 2019, when it restricted tweets from journalists and government accounts in Cuba following President Miguel Diaz-Canel’s address regarding an energy crisis exacerbated by US sanctions. This move drew criticism, with concerns raised over potential censorship and selective enforcement of platform manipulation policies.
In the Indian context, despite evidence suggesting widespread misuse of social media for propagating misinformation, Twitter’s response has been perceived as inadequate. Reports indicate the existence of thousands of fake accounts amplifying fake news, particularly associated with major political parties like the BJP and Congress. Despite such findings, Twitter has yet to take decisive action comparable to its response in other regions.
Furthermore, Twitter’s compliance with government directives, such as the removal of tweets critical of the Indian government in Kashmir and the withholding of Kashmiri accounts in India, has sparked controversy. Critics argue that such actions raise questions about Twitter’s commitment to free expression and its impartiality in addressing sensitive geopolitical issues.
Moreover, Twitter has faced criticism for its perceived inaction against instances of online abuse, particularly those rooted in misogyny and casteism. This perceived bias has prompted some users to explore alternative platforms like Mastodon in protest.
Twitter’s move to flag Amit Malviya’s tweet as ‘manipulated media’ signifies a step towards holding political figures accountable for deceptive content. However, questions persist regarding the platform’s consistency in enforcing such policies, especially in contexts like India where the spread of misinformation is a pressing concern.