India’s ruling party, the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), is sometimes said to prioritize Hindu interests. Hindus were the religious group most likely to say they voted for the BJP in the country’s most recent parliamentary election, but there are vast differences in how Hindus from different regions voted, according to a recent Pew Research Center survey of nearly 30,000 Indian adults. These regional political differences are connected to Hindu attitudes on a range of issues including language, diet and religious observance.
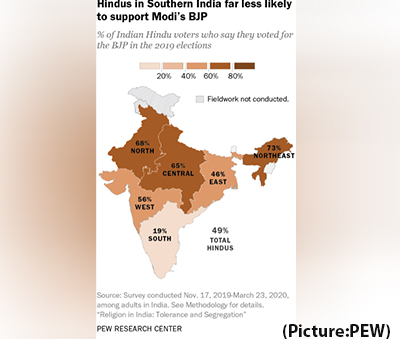 How we did this In 2019, roughly half of Hindu voters (49%) supported the BJP, giving the party a majority in the Lok Sabha – India’s lower house of parliament – and allowing Prime Minister Narendra Modi a second term to lead the country. Among Hindus, the BJP received some of its highest vote shares in the Northern (68%) and Central (65%) regions of the country, which include India’s capital, Delhi, and its most populous state, Uttar Pradesh. By comparison, 46% of Hindu voters in the East and just 19% in the South say they voted for the BJP, according to the Center’s survey.
How we did this In 2019, roughly half of Hindu voters (49%) supported the BJP, giving the party a majority in the Lok Sabha – India’s lower house of parliament – and allowing Prime Minister Narendra Modi a second term to lead the country. Among Hindus, the BJP received some of its highest vote shares in the Northern (68%) and Central (65%) regions of the country, which include India’s capital, Delhi, and its most populous state, Uttar Pradesh. By comparison, 46% of Hindu voters in the East and just 19% in the South say they voted for the BJP, according to the Center’s survey.
In the South, significant shares of Hindu voters (20%) say they instead supported the Indian National Congress (INC), which has led the country for most of the years since its independence. Regional parties, including the Telangana Rashtra Samithi and the Yuvajana Sramika Rythu Congress Party, also received significant vote shares among Southern Hindus (both 11%). Southern states tend to have higher per capita income and have experienced faster economic growth than most Northern and Central states. Differences in voting patterns between Southern Hindus and those who live in the Northern and Central regions are part of broader regional differences among Hindus in India. For example, Hindu nationalist sentiments appear to have a smaller foothold in the South. Nationally, 64% of Hindus in India say being a Hindu is very important to being truly Indian. But while this share is as high as 83% in the Central region, it falls to 42% in the South.
A closely related sentiment is the importance of the Hindi language to national identity: The majority of Hindus in the Central (87%) and Northern (71%) regions say that speaking Hindi is very important to being truly Indian, while just 27% of Southern Hindus say this. Among the dozens of commonly spoken Indian languages, Hindi is the most widespread. However, while it is often spoken in the Northern and Central parts of the country, it is far less common in the South. Views on the connection between the Hindu religion, Hindi language and Indian identity are highly correlated with support for the BJP – a party that has supported making Hindi the national language and has enacted laws (such as restricting cow slaughter) that are seen as favorable to Hindus.
Indeed, attitudes about cow slaughter and beef consumption mark another division between the South and other regions of the country. Many Hindus consider cows sacred animals, but there are mixed views about whether eating beef disqualifies a person from being a Hindu. Most Hindus in the Northern and Central regions (both 83%) say someone who eats beef cannot be Hindu, compared with half of Southern Hindus. And attitudes about beef and Hindu identity are correlated with support for the BJP: Hindus who say they voted for the BJP are more likely than other Hindu voters to say someone who eats beef cannot be Hindu (77% vs. 66%). Southern Hindus also differ in their religious observance. For instance, while 92% of Hindus in the Central region say religion is very important in their life, the share is substantially lower among Southern Hindus (68%). More religious Hindus tend to support the country’s ruling party: About half of Hindus who say religion is very important in their lives (52%) voted for the BJP in 2019, compared with around a third of Hindus (32%) who say religion is less important in their lives.
Views of the BJP differ along other religious lines in India, too. Among minority religions analyzed in the Center’s report, Jains appear to be the only group who strongly embrace the BJP. While the survey did not include enough Jain voters to report how they voted in the 2019 election, 70% of Jains said in a separate question that they feel closest to the BJP, regardless of whether they voted in the last election. Meanwhile, other religious groups showed less support for the ruling party: Fewer than a third of Buddhists (29%), Muslims (19%), Sikhs (19%) and Christians (10%) say they voted for the BJP in the 2019 parliamentary election.
Many voters from minority religions opted to vote for parties other than the BJP or INC. For example, 14% of Buddhists say they voted for the Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP), a national party focused primarily on the welfare of lower castes and minority religions; 89% of Buddhists are members of Scheduled Castes. Support for regional parties is also tied to religion. For instance, 16% of Sikhs say they voted for Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) in 2019. SAD is a regional party representing Punjabi interests; according to the most recent national census, conducted in 2011, 77% of India’s Sikhs live in Punjab.











