The number of children and teens killed by gunfire in the United States increased 50% between 2019 and 2021, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of the latest annual mortality statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
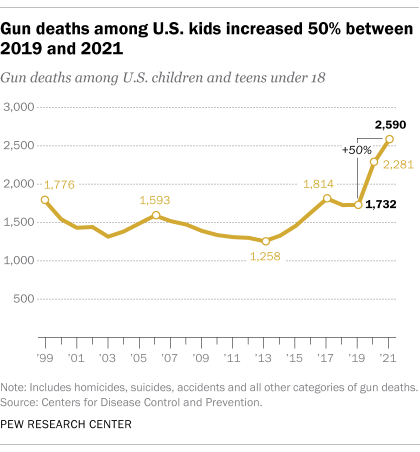 In 2019, before the coronavirus pandemic, there were 1,732 gun deaths among U.S. children and teens under the age of 18. By 2021, that figure had increased to 2,590.
In 2019, before the coronavirus pandemic, there were 1,732 gun deaths among U.S. children and teens under the age of 18. By 2021, that figure had increased to 2,590.
The gun death rate among children and teens – a measure that adjusts for changes in the nation’s population – rose from 2.4 fatalities per 100,000 minor residents in 2019 to 3.5 per 100,000 two years later, a 46% increase.
Both the number and rate of children and teens killed by gunfire in 2021 were higher than at any point since at least 1999, the earliest year for which information about those younger than 18 is available in the CDC’s mortality database.
How we did this
The rise in gun deaths among children and teens is part of a broader recent increase in firearm deaths among Americans overall. In 2021, there were 48,830 gun deaths among Americans of all ages – by far the highest yearly total on record and up 23% from the 39,707 recorded in 2019, before the pandemic.
The total number of gun deaths among children and teens in 2021 includes homicides, suicides, accidents and all other categories where firearms are listed on death certificates as the underlying cause of death. It does not include deaths where firearms are listed as a contributing, but not underlying, cause of death.
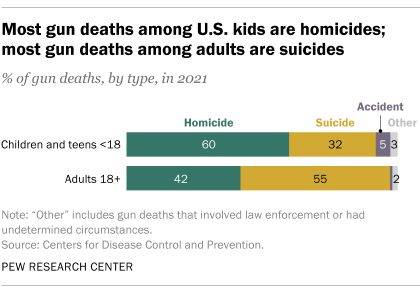 Homicide was the largest single category of gun deaths among children and teens in 2021, accounting for 60% of the total that year. It was followed by suicide at 32% and accidents at 5%. Among U.S. adults, by contrast, suicides accounted for a 55% majority of gun deaths in 2021.
Homicide was the largest single category of gun deaths among children and teens in 2021, accounting for 60% of the total that year. It was followed by suicide at 32% and accidents at 5%. Among U.S. adults, by contrast, suicides accounted for a 55% majority of gun deaths in 2021.
In addition to data on gun fatalities, the CDC publishes estimates on nonfatal gun-related injuries sustained by children and teens. In 2020 – the most recent year with available data – there were more than 11,000 emergency-room visits for gunshot injuries among children and teens under the age of 18 – far higher than in other recent years. An exact count is not possible, however, because the CDC’s estimate is based on a sample of U.S. hospitals, not all U.S. hospitals, and is subject to a large margin of error.
Gun deaths are much more common among some groups of children and teens
In the U.S., some groups of children and teens are far more likely than others to die by gunfire. Boys, for example, accounted for 83% of all gun deaths among children and teens in 2021. Girls accounted for 17%.
Older children and teens are much more likely than younger kids to be killed in gun-related incidents. Those ages 12 to 17 accounted for 86% of all gun deaths among children and teens in 2021, while those 6 to 11 accounted for 7% of the total, as did those 5 and under. Still, there were 179 gun deaths among children ages 6 to 11 and 184 among those 5 and under in 2021.
For all three age groups, homicide was the leading type of gun death in 2021. But suicides accounted for a significant share (36%) of gun deaths among those ages 12 to 17, while accidents accounted for a sizable share (34%) of gun deaths among those 5 and under.
Racial and ethnic differences in gun deaths among kids are stark. In 2021, 46% of all gun deaths among children and teens involved Black victims, even though only 14% of the U.S. under-18 population that year was Black. Much smaller shares of gun deaths among children and teens in 2021 involved White (32%), Hispanic (17%) and Asian (1%) victims.
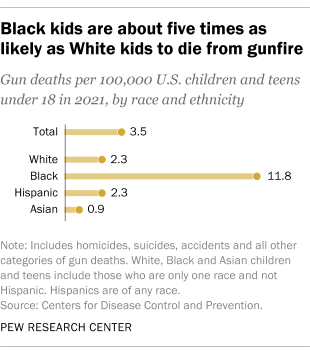 Looked at another way, Black children and teens were roughly five times as likely as their White counterparts to die from gunfire in 2021. There were 11.8 gun deaths per 100,000 Black children and teens that year, compared with 2.3 gun deaths per 100,000 White children and teens. The gun death rate among Hispanic children and teens was also 2.3 deaths per 100,000 in 2021, while it was lower among Asian children and teens (0.9 per 100,000).
Looked at another way, Black children and teens were roughly five times as likely as their White counterparts to die from gunfire in 2021. There were 11.8 gun deaths per 100,000 Black children and teens that year, compared with 2.3 gun deaths per 100,000 White children and teens. The gun death rate among Hispanic children and teens was also 2.3 deaths per 100,000 in 2021, while it was lower among Asian children and teens (0.9 per 100,000).
There are also major racial and ethnic differences in the types of gun deaths involving children and teens. In 2021, a large majority of gun deaths involving Black children and teens (84%) were homicides, while 9% were suicides. Among White children and teens, by contrast, the majority of gun deaths (66%) were suicides, while a much smaller share (24%) were homicides.
In this analysis, Black, White and Asian children and teens include only those who are single-race and not Hispanic, while Hispanic children and teens are of any race.
Nearly half of U.S. parents worry about their children getting shot
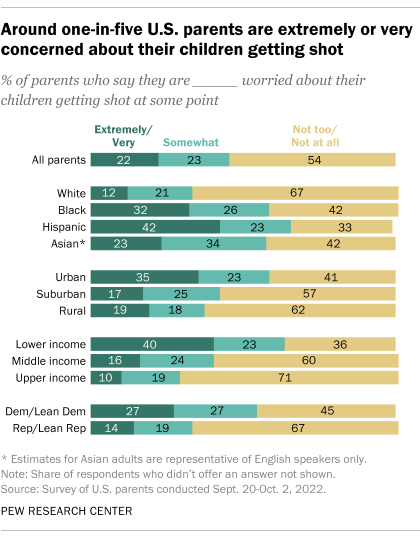 A sizable share of American parents are worried about their kids getting shot. In a fall 2022 Pew Research Center survey, 22% of parents with children under 18 said they were extremely or very worried about any of their children getting shot at some point, while another 23% said they were somewhat worried. Still, more than half said they were not worried about this.
A sizable share of American parents are worried about their kids getting shot. In a fall 2022 Pew Research Center survey, 22% of parents with children under 18 said they were extremely or very worried about any of their children getting shot at some point, while another 23% said they were somewhat worried. Still, more than half said they were not worried about this.
The survey found demographic differences in these concerns. Around four-in-ten Hispanic parents (42%) and about a third of Black parents (32%) said they were extremely or very worried about their children getting shot, compared with smaller shares of Asian (23%) and White (12%) parents.
Parents in self-described urban communities (35%) were considerably more likely than those in rural (19%) or suburban (17%) areas to be extremely or very worried about any of their children being shot. And lower-income parents (40%) were far more likely than middle-income (16%) and upper-income (10%) parents to be extremely or very worried.
Partisan differences were evident, too. Democratic and Democratic-leaning parents were roughly twice as likely as Republican and Republican-leaning parents to say they were extremely or very worried about their children getting shot at some point (27% vs. 14%). )PEW Research)
