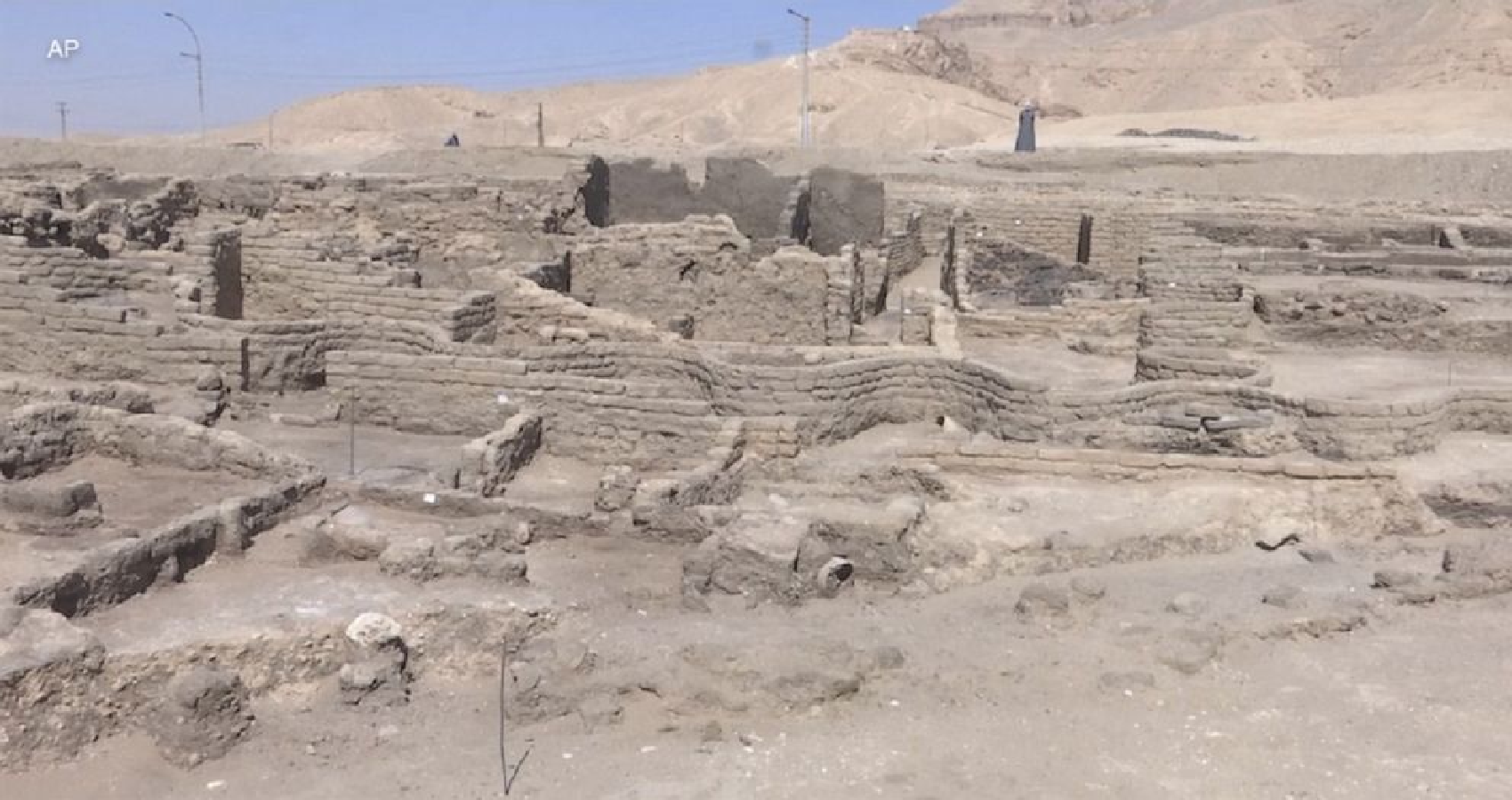
A 3,000-year-old “lost golden city” has been unearthed in the southern city of Luxor, a discovery that could be the most significant find in Egypt since the tomb of the boy king Tutankhamen, an archaeological mission said on April 8, 2021) in a statement.
Archaeologists have hailed the discovery of what is believed to be the largest ancient city found in Egypt, buried under sand for millennia, which experts said was one of the most important finds since the unearthing of Tutankhamun’s tomb. The famed Egyptologist Zahi Hawass announced the discovery of the “lost golden city”, saying the site was uncovered near Luxor, home of the Valley of the Kings.
“The Egyptian mission under Dr Zahi Hawass found the city that was lost under the sands,” the archeology team said. “The city is 3,000 years old, dates to the reign of Amenhotep III, and continued to be used by Tutankhamun and Ay.” It called the find the largest ancient city, known as Aten, ever uncovered in Egypt.
Aten is believed to have been founded by King Amenhotep III, the ninth king of ancient Egypt’s 18th dynasty who ruled the country from 1391 to 1352 B.C., the mission’s statement said. It is believed to be that era’s largest administrative and industrial settlement, nestled on the western bank of Luxor.
“The discovery of this lost city is the second most important archaeological discovery since the tomb of Tutankhamen,” Betsy Bryan, an Egyptology professor at Johns Hopkins University and member of the mission, said in the statement. Its discovery “will give us a rare glimpse into the life of the ancient Egyptians” when the empire was at its wealthiest.
The lost city is the latest in a series of archaeological discoveries unearthed in recent months across the country that are bringing fresh understanding of the dynasties that ruled ancient Egypt. Egypt’s government hopes that such findings will bolster the nation’s all-important tourism industry, battered in recent years by the coronavirus pandemic, Islamist militant attacks and political instability.
Aten promises to be among the most significant of the recent finds.
 Archaeologists started excavating in September in the area between the temples of King Ramses III and Amenhotep III. The original goal of the mission was to find King Tutankhamen’s mortuary temple, the statement said.
Archaeologists started excavating in September in the area between the temples of King Ramses III and Amenhotep III. The original goal of the mission was to find King Tutankhamen’s mortuary temple, the statement said.
“Within weeks, to the team’s great surprise, formations of mud bricks began to appear in all directions,” the statement said. “What they unearthed was the site of a large city in a good condition of preservation, with almost complete walls, and with rooms filled with tools of daily life.
“The archaeological layers have [lain] untouched for thousands of years, justify by the ancient residents as if it were yesterday,” it said. “Many foreign missions searched for this city and never found it,” Zahi Hawass, an Egyptian archaeologist and former minister of state for antiquities affairs who led the mission, said in the statement.
The city was active during the reign of Amenhotep III as well as during his co-regency with his son, Amenhotep IV, also known as Akhenaton. The city was later used by Tutankhamen and his successor, King Ay. Hawass said the city’s streets are flanked by houses, some of which have walls nearly 10 feet high.
The archaeological team dated the settlement through hieroglyphic inscriptions found on wine vessels, rings, scarabs, pottery and mud bricks bearing the seals of King Amenhotep III’s cartouche, the statement said. “Work is underway and the mission expects to uncover untouched tombs filled with treasures,” the statement read.